5 key facts about this project
## Analytical Report on Tokyo PopLab Architectural Design Project
### Overview
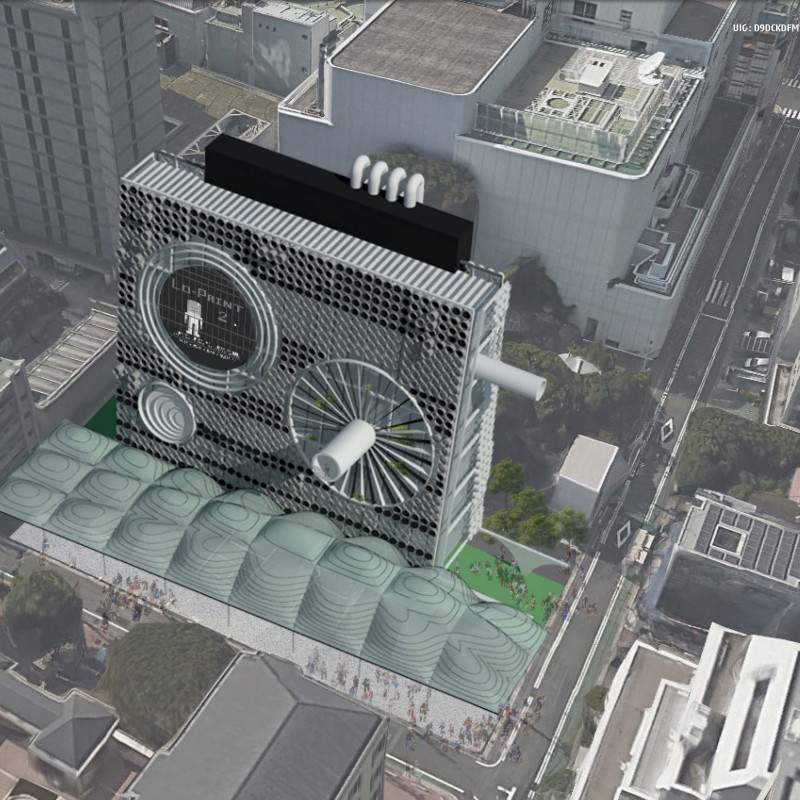
Located in Tokyo, Japan, the PopLab project serves as a multifunctional space aimed at fostering creativity, collaboration, and community engagement through its innovative architectural design. The intent is to create an environment that attracts a diverse user base, including students, professionals, and families. By reflecting modern aesthetic sensibilities and technological advancements, the project is positioned to enhance the urban landscape and promote innovative interactions.
### Structural and Spatial Configuration
The architectural layout incorporates both private and communal areas to support a range of activities. The ground floor functions as an interactive hub, featuring an exhibition hall designed to invite public engagement. Its dynamic façade, characterized by a hexagonal pattern and protruding elements, draws attention and encourages exploration. Intermediate levels are designated for educational functions, including lecture rooms, workshops, and a library, allowing for adaptability to various events and user requirements. Additionally, a rooftop café serves as a communal space with panoramic views, enhancing social interaction among users. The overall configuration emphasizes accessibility and fosters a connection between users and their environment.
### Material Selection and Ecological Integration
Key materials have been deliberately chosen to contribute to the project's identity and functionality. Steel provides the structural framework, ensuring stability and durability. Glass enhances transparency and natural lighting, creating visual connections to the exterior. Polycarbonate elements offer lightweight surfaces that align with the playful aesthetic, while concrete serves as the foundation and flooring material for robustness. Sustainability is addressed through the incorporation of green roof systems that manage rainwater and promote biodiversity. This mindful selection of materials facilitates a dialogue between the building and its urban surroundings, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and ecological responsibility.