5 key facts about this project
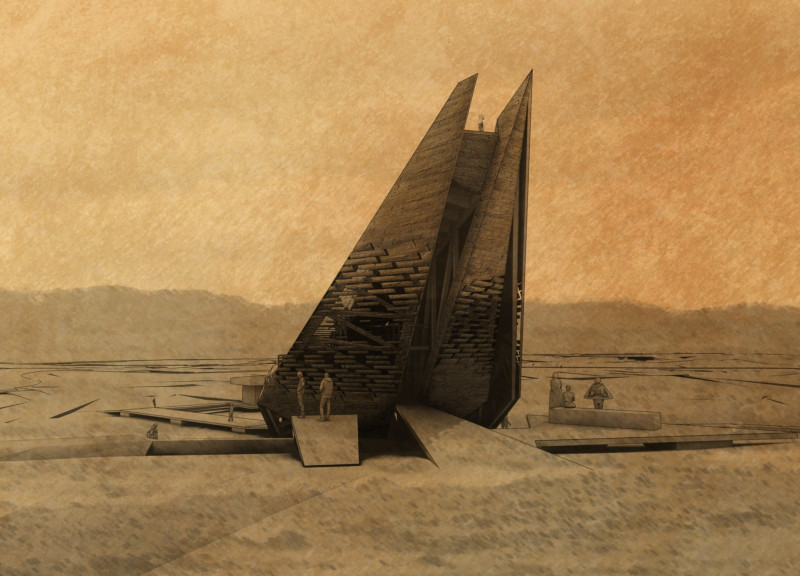
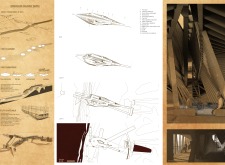
The structure exhibits an angular silhouette, with a tilted tower that appears to emerge organically from the earth. This form fosters a connection between the interior and the surrounding landscape, enhancing the building's presence within its environment. Visitors are encouraged to explore the exterior and interior, which feature various levels and platforms, promoting interaction with the terrain.
Sustainable practices are central to the project. The use of materials such as reclaimed structural steel, basalt, and local timber emphasizes a commitment to reducing environmental impact. The geothermal plant within the building allows for energy independence, reflecting contemporary architectural trends toward sustainability.
Architectural Features and Unique Design Approaches
The Grjótága project distinguishes itself through its environmental integration and innovative use of materials. The chosen form correlates with the surrounding landscape, while the interior spaces are designed for maximum exploration and interaction. This approach not only caters to aesthetics but also creates a practical environment for guests. The building’s layout incorporates geothermal heating, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
This project also takes into account the site’s geological context. Its design acknowledges the tectonic activities nearby, designing spaces that resonate with the natural geothermal elements around them. This sensibility is an integral part of the architectural philosophy that shapes Grjótága, making it a relevant model for future developments in similar environments.
Functional Design and Spatial Considerations
Grjótága serves as a retreat, offering observation platforms for guests to engage with their surroundings meaningfully. The interior layout supports a variety of activities that take advantage of the site's unique aspects. Architectural sections detail spaces that cater to both relaxation and exploration, enhancing users’ experiences while promoting the benefits of sustainable living.
The use of native materials not only ties the structure aesthetically to its environment but also serves practical functions, such as thermal stability and durability. Wood, basalt, and steel interact synergistically, ensuring that the architecture embodies the principles of resilience while providing a visually coherent and functional space.
To gain further insights into the architectural concepts underpinning Grjótága, readers are encouraged to explore the detailed architectural plans and sections available for review. Understanding the design elements and architectural strategies implemented throughout this project enhances appreciation for its thoughtful integration with the surrounding landscape and sustainability goals.