5 key facts about this project
Integration of Natural and Built Environments
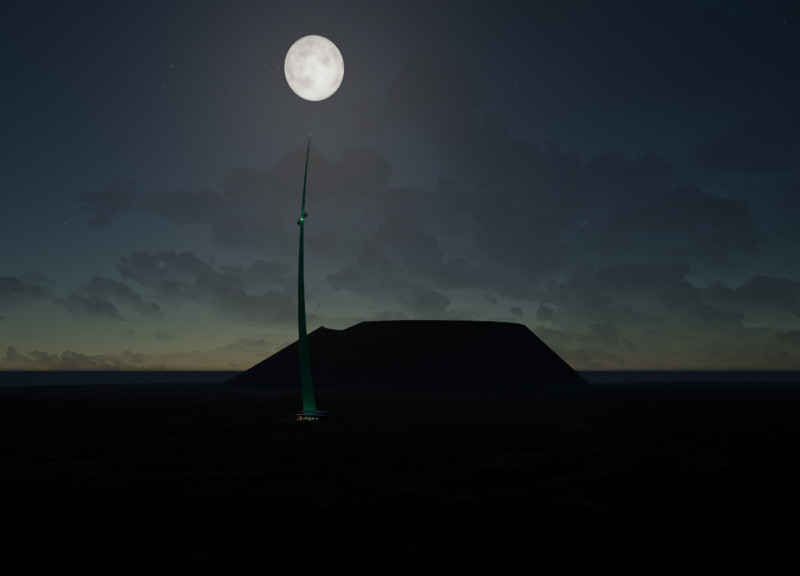
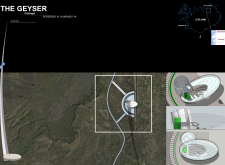
What sets The Geyser apart from conventional architectural projects is its direct reflection of geothermic phenomena, taking design cues from the eruption patterns of geysers. The building's silhouette resembles a geyser’s plume, creating a visual dialogue with the landscape. The design prioritizes sustainability, incorporating locally sourced materials such as concrete, steel, timber, glass, and stone, ensuring a minimal environmental footprint and a strong connection to the site.
The strategic layout includes multiple observation decks and public amenities, enhancing accessibility while fostering educational opportunities regarding geothermal energy. The ground level features an expansive plaza that invites exploration, while elevated vantage points offer unobstructed views of geysers and the surrounding topography.
Innovative Use of Materials
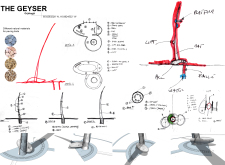
The Geyser employs a blend of advanced and traditional materials to reinforce its architectural intent. Concrete forms the foundational structure, ensuring durability against the harsh environmental conditions typical of Iceland, while steel elements are utilized for their strength and resilience. Wood is incorporated to soften the aesthetic and provide warmth, contrasting the cold, stark elements of stone and concrete. Large glass panels enable extensive natural light and provide panoramic views, minimizing the separation between the interior spaces and the external landscape.
The integration of sustainable technologies, such as solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems, further highlights the design's commitment to energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. These innovations contribute to both the building's functionality and its educational mission, teaching visitors about the potential of renewable energy sources.
User Experience and Educational Focus
This project is fundamentally designed to enhance the visitor experience. It uses interactive installations that educate visitors about geothermal energy, the geological aspects of the area, and the cultural significance of these natural phenomena. Paths and walkways lead through the landscape, maintaining a direct connection to the surrounding natural beauty while reinforcing the structural theme of the geyser.
The varying levels of the structure allow for diverse visitor interactions with the site; those who seek direct engagement with geothermal activity can find secure observation areas designed for safety and comfort. This careful consideration of user experience adds a layer of depth to the project's architectural narrative.
For detailed insights into The Geyser project, including architectural plans, sections, designs, and innovative ideas, readers are encouraged to explore the project presentation further. The thorough examination of its design elements will provide a comprehensive understanding of its contribution to contemporary architecture within the unique context of Iceland's geothermal landscape.