5 key facts about this project
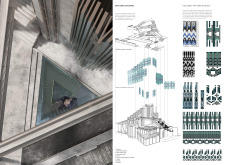
The museum functions as both an educational and experiential venue, featuring exhibition halls and observation platforms that allow visitors to engage with the natural environment. The design emphasizes the interplay between the building and its landscape, enabling visitors to appreciate the geological features of Iceland from various vantage points. The structure facilitates efficient circulation and access, ensuring that visitors experience the exhibits in a coherent narrative flow.
Unique Architectural Approaches
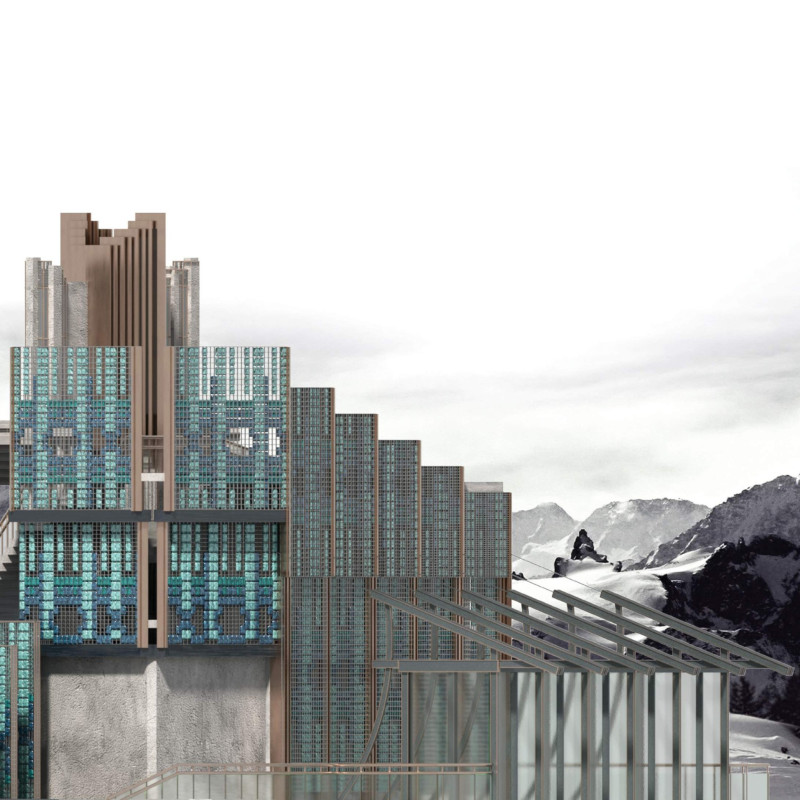
One of the project's most notable features is its geometric expression, which draws directly from the surrounding landscape's contours and textures. The building’s facade employs angular forms and stepped profiles that mimic the rugged terrain, allowing it to blend into the environment while providing a visually engaging experience. The incorporation of windows and glass walls maximizes natural light and fosters a connection between the interior and exterior spaces, allowing visitors to feel immersed in the geological narrative of the surroundings.
The design prioritizes sustainability through the use of locally sourced materials, which not only reduce the carbon footprint but also promote an understanding of the local context. Additionally, the building's potential for geothermal energy utilization aligns with Iceland's contemporary architectural practices that embrace sustainability. By carefully selecting materials that reflect both durability and aesthetic value, the project fosters a sense of place that enhances the visitor experience.
Spatial Organization and Functional Elements
The museum’s layout is organized around key functional areas, including exhibition spaces, visitor facilities, and observation points. The interior design accommodates diverse exhibit types by providing adaptable spaces capable of hosting static displays and interactive installations. This flexibility is crucial for engaging a broad audience and facilitating educational programming.
Observation platforms are strategically included in the design to offer unobstructed views of the surrounding geology. These areas encourage visitors to engage with the landscape, fostering a deeper appreciation of the geological story that underpins the museum’s mission. The combination of dynamic spaces and thoughtful materials enables the museum to fulfill its function as an educational facility while remaining sensitive to the natural environment.
For a comprehensive understanding of the Cairns Stone Museum, including architectural plans, sections, designs, and ideas, readers are encouraged to explore the full project presentation. The detailed insights into this architectural endeavor can provide valuable perspectives on the integration of human-made structures with the natural landscape.