5 key facts about this project
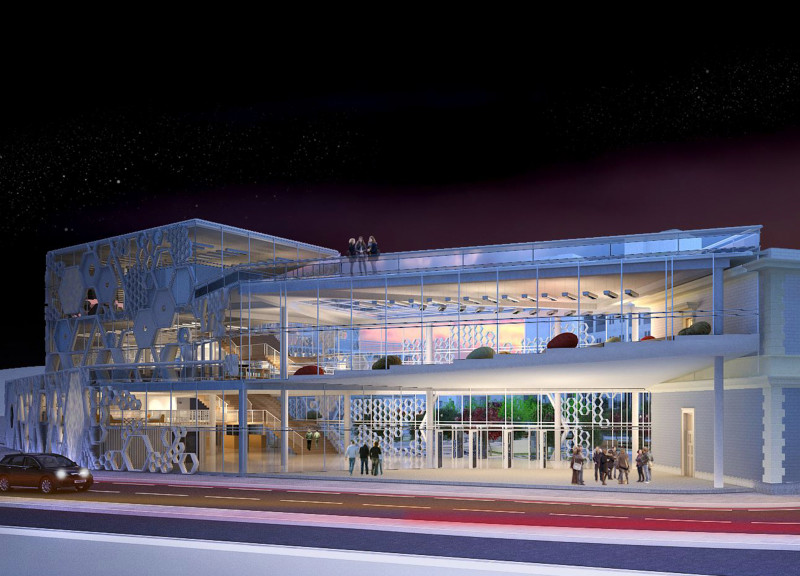
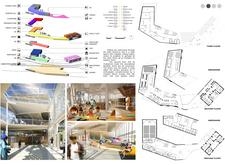
The architecture of HUB-M is characterized by its transparent facade, predominantly made of glass panels, which symbolizes openness and accessibility. This design invites natural light into the interior, creating a welcoming atmosphere for visitors. The extensive use of glass not only represents the clarity and visibility of information in the digital world but also blurs the boundaries between the museum's interior and the surrounding urban landscape, inviting passersby to engage with the space.
In terms of structure, the building features a hexagon-based metal framework, potentially utilizing aluminum or steel. This choice of material is not only functional but also conveys a sense of modernity and innovation. The hexagonal pattern serves as a metaphor for digital networks and relationships, echoing the interconnectedness found within the digital realm. The choice of concrete for structural supports ensures durability while complementing the contemporary aesthetic of the museum.
The design incorporates varied functional zones that enhance visitor experience. The ground floor is designed as a vibrant entry point featuring a café, restaurant, museum shop, and car park, making it an accessible space for community gatherings. Moving up, the second floor is likely dedicated to educational facilities that cater to tech enthusiasts, while the third floor and mezzanines provide flexible exhibition spaces and leisure areas. This thoughtful zoning encourages exploration and uses architectural design to foster interaction among visitors.
One of the unique approaches seen in the HUB-M Internet Museum is its emphasis on adaptability and flexibility. The interactive exhibition hall is designed with movable panels and technology integration, allowing for a constantly evolving exhibition experience. This responsiveness to content is crucial in a museum dedicated to digital culture, where information and technology are in a state of perpetual change. The integration of outdoor terraces and open spaces further promotes public interaction, serving as gathering points for events and informal meetings.
Furthermore, HUB-M demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, which is increasingly relevant in contemporary architectural design. While specific sustainable elements such as green roofs or solar panels were not explicitly mentioned, the project’s design principles align with modern trends that prioritize environmental consciousness without sacrificing aesthetic appeal.
The architectural approach taken in the HUB-M Internet Museum reflects a mindful engagement with both the historical context and contemporary needs of users. By creating an inviting, adaptable space dedicated to exploring digital culture, this project encourages deeper connections among individuals and between the physical and digital worlds. By delving into the architectural plans and sections, the reader can gain valuable insights into how each design choice contributes to the overall experience of the museum. Exploring the architectural designs and ideas behind the HUB-M allows one to appreciate the nuances that make it a relevant addition to its urban context. For those intrigued, further exploration of the project presentation is encouraged to discover more about its intricate architectural details and the vision behind this engaging space.