5 key facts about this project
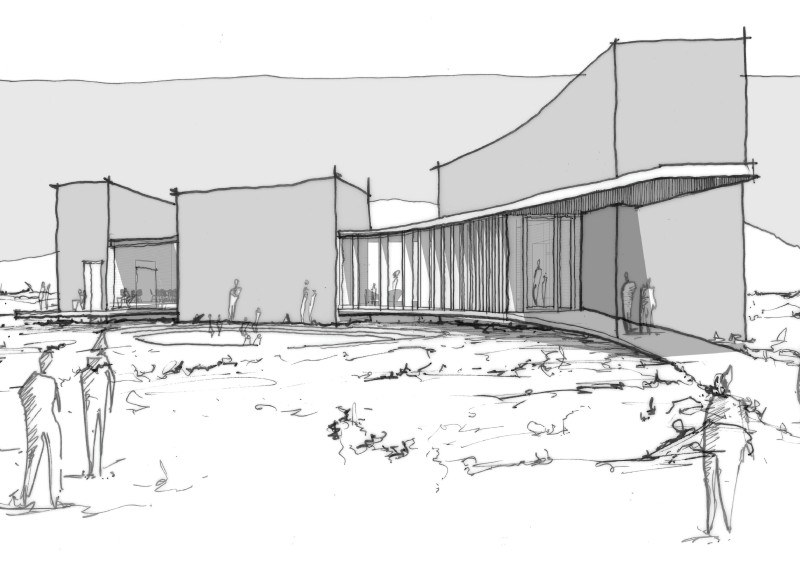
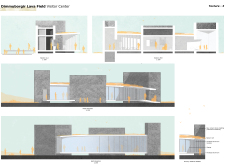
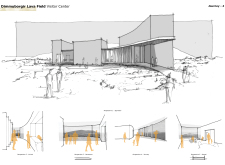
The Visitor Center’s design concept emphasizes the interplay between the built environment and the natural landscape. By drawing inspiration from the forms of craters and lava flows, the architecture integrates seamlessly into its surroundings. The building materials enhance this connection; raw volcanic stone clads the structure, mirroring the geological features nearby. The large glass facades serve a dual purpose, allowing natural light to flood the interior while framing views of the significant geological formations, thus creating an immersive visitor experience.
Unique Design Approaches
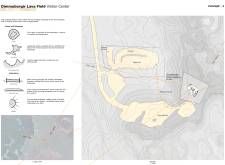
One of the distinguishing characteristics of the Dimmuborgir Visitor Center is its curvilinear architectural style, which deviates from the traditional rigid structures often found in similar projects. The design allows the building to blend into the undulating terrain, with sweeping lines reflecting the dynamism of lava flows. Terraces and viewing platforms extend outwards, encouraging visitors to engage directly with the landscape. This spatial strategy not only facilitates a deeper connection with the environmental context but also maximizes visual interaction between indoor activities and outdoor vistas.
Sustainability is also a key aspect of the design approach. The use of a sedum roof contributes to ecological balance by providing insulation and enhancing the building's integration with the natural surroundings. The materials selected for construction, including anodized aluminum for window frames, also support durability, ensuring the structure can withstand the harsh Icelandic climate while maintaining its aesthetic integrity.
Architectural Details and Functionality
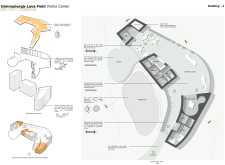
The layout of the Visitor Center is organized into functional zones, including a lobby, exhibition spaces, a café, and educational areas. Each zone is designed to facilitate specific visitor interactions while promoting a cohesive flow throughout the building. The lobby serves as the central hub, providing access to all areas and displaying views of the lava formations. The café is strategically placed to enable visitors to appreciate the landscape while relaxing.
Exhibition spaces are designed to provide interactive experiences, presenting both the geological history and the cultural narratives of the region. These areas are equipped with displays that allow for a multifaceted exploration of Dimmuborgir, encouraging deeper engagement with its natural and cultural significance.
For those interested in exploring more about the Dimmuborgir Lava Field Visitor Center, a review of the architectural plans, sections, and designs will offer deeper insights into the project’s structural and aesthetic considerations. This analysis invites further investigation into how the architectural ideas manifest in this unique setting.