5 key facts about this project
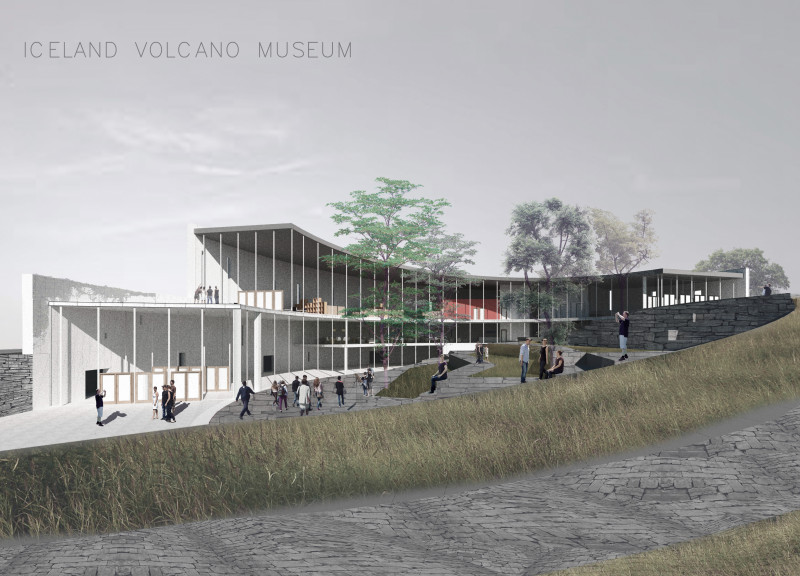
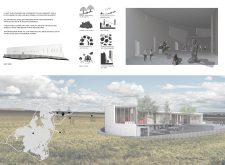
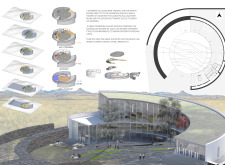
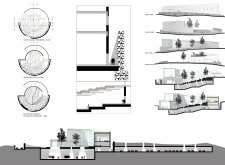
The architectural design features a series of curved lines and dynamic forms that evoke the organic shapes of lava flows. The museum’s facade combines concrete and glass, allowing for an interplay of light and space. The structure is oriented to maximize views of the landscape, emphasizing its connection to the natural environment. The interior spaces are flexible and adaptable, capable of accommodating various exhibition formats.
Materials used in the project include locally sourced concrete, high-performance glass, natural stone, and wood. Each material was selected not only for its performance characteristics but also for its ability to integrate the building harmoniously with its location. The use of local stone for outdoor pathways reinforces the museum's relationship with the surrounding environment, creating continuity between the built and natural worlds.
The museum prioritizes environmental sustainability through its design decisions. The building incorporates passive heating and cooling strategies to reduce energy consumption and utilizes natural light to enhance visitor experiences. This commitment to sustainability is a significant aspect of the project, setting it apart from other cultural facilities in similar contexts.
Unique design approaches within the Iceland Volcano Museum include its integration of public spaces that promote interaction and community involvement. The design incorporates an amphitheater for performances and public gatherings, a feature that extends the museum’s function beyond a traditional educational facility. The layout encourages visitors to explore and engage with the exhibits, fostering a deeper understanding of Iceland’s volcanic heritage.
Additionally, the landscape design is a critical component of the overall project. The museum grounds feature native vegetation, contributing to local biodiversity while providing visitors with an immersive natural experience. The design of walking paths reflects the textures of volcanic terrain, guiding visitors through the space while reinforcing its geological context.
Overall, the Iceland Volcano Museum stands as an example of how architecture can effectively bridge education, community, and environmental awareness. To gain deeper insights into this innovative project, it is recommended to explore the architectural plans, sections, and designs presented in the full project documentation. This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of its layout, functionality, and unique architectural ideas.