5 key facts about this project
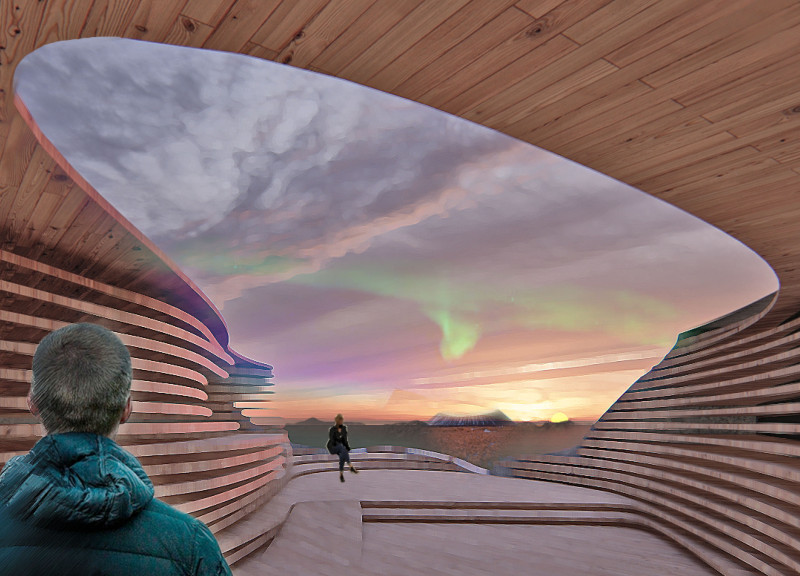
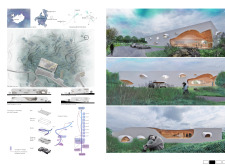
The structure features a combination of sustainable timber, concrete, glass, and natural stone, each carefully selected to enhance both durability and the visual impact of the guest house. The use of natural materials provides warmth and engages with the local architecture, while large glass facades invite natural light and views of the landscape.
Unique Design Approaches
The Iceland Guest House stands out through its fluid design that reflects the undulating topography of the region. Instead of adhering to conventional rectangular forms, the architecture embraces curves and organic shapes that mirror the Icelandic terrain. This approach not only provides a distinct visual character but also fosters a sense of place, aligning the design closely with its geographical context.
Key features include flexible interior layouts that cater to various accommodation requirements and communal spaces that encourage social interaction among guests. Observation decks and terraces integrated into the design allow for panoramic views, providing spaces for both relaxation and contemplation. The architectural choices made throughout the project also address sustainability, with passive design strategies enhancing energy efficiency and indoor climate control.
Innovative Materials and Construction Techniques
The construction of the Iceland Guest House utilizes a diverse range of materials that contribute to its overall functionality and aesthetic. Sustainable timber forms the primary structural framework, promoting environmental responsibility. Concrete elements ensure stability while allowing for intricate geometric designs. The extensive use of glass emphasizes transparency and connectivity between interior and exterior spaces. Natural stone is employed for outdoor areas, reinforcing the connection between the building and its rugged landscape.
The architectural design is also characterized by its commitment to energy efficiency. The building's orientation, thermal mass construction, and natural ventilation strategies work together to minimize energy consumption. These considerations contribute not only to the project's sustainability but also to the comfort of its occupants.
For a comprehensive understanding of the Iceland Guest House project, including its architectural plans, sections, designs, and underlying ideas, further exploration of the presentation is recommended. Engaging with these elements will provide deeper insights into the design principles and unique approaches employed throughout the project.