5 key facts about this project
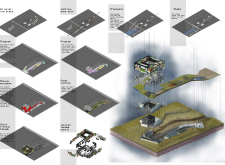
The museum serves multiple functions, including exhibition spaces, community gathering areas, and educational facilities. The architectural concept utilizes a series of interconnected spaces, allowing for a cohesive visitor flow while providing distinct zones for various activities. The project emphasizes sustainability and uses environmentally friendly materials and design approaches to minimize the ecological footprint.
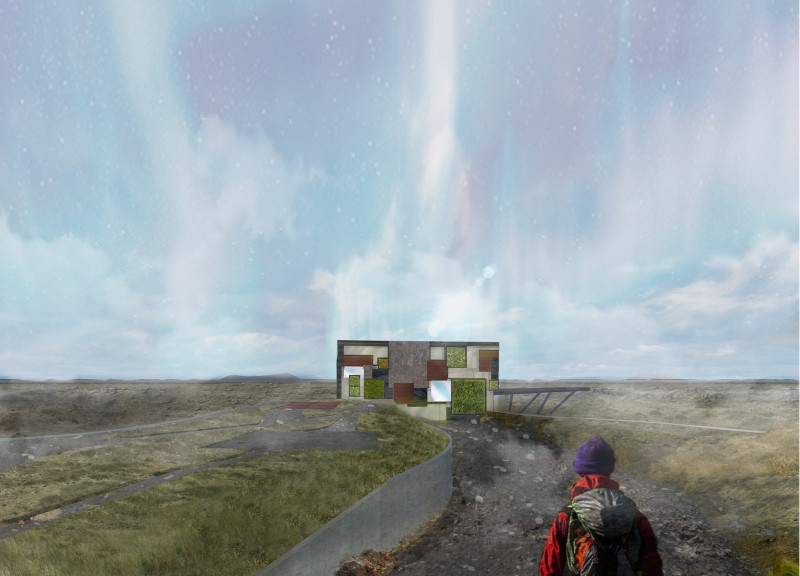
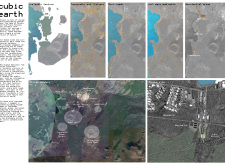
One of the unique design approaches of "Cubic Earth" lies in its responsive architectural elements. Large expanses of glass play a critical role in connecting indoor spaces with the outdoors, offering panoramic views of the picturesque landscape. The implementation of a green roof serves both aesthetic and functional purposes, promoting biodiversity while providing insulation and reducing energy consumption. This thoughtful integration of natural elements into the design encourages visitors to engage with their surroundings actively.
The design also includes architectural features that reflect local building traditions while representing contemporary architectural practices. The use of materials such as locally sourced stone, wood, and concrete creates a dialogue between the structure and its environment. The cubic form of the museum draws parallels with Iceland's geological landscape, reinforcing the connection between architecture and nature.
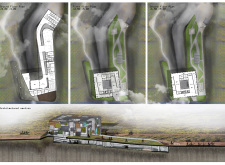
The museum layout comprises three levels, with each floor dedicated to specific functions. The ground floor accommodates entry and orientation spaces, while the upper levels house exhibition halls and educational areas. This tiered approach ensures that visitors can navigate the building smoothly while experiencing a progression of spaces and interactions.
For those interested in exploring more about "Cubic Earth," including architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs, a detailed project presentation is available for further insights into this thoughtful and contextually relevant architectural endeavor. The combination of innovative design ideas and a deep respect for the natural landscape makes this project a noteworthy example of contemporary architecture in Iceland.