5 key facts about this project
### Overview
Located in the United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future is designed according to the LOHAS (Lifestyles of Health and Sustainability) philosophy. The project aims to create a sustainable living environment that effectively integrates natural elements with advanced technology, prioritizing energy efficiency and wellness for its inhabitants.
### Spatial Configuration
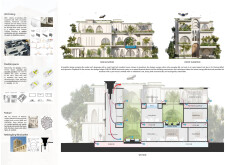
The architectural design features a fluid spatial arrangement highlighted by an open-air courtyard, facilitating continuity between indoor and outdoor spaces to enhance comfort and natural ventilation. Flexible living areas are crafted with movable partitions, allowing for customization according to the occupants' needs. This adaptability accommodates diverse living arrangements, including families and multi-generational units, while separating functional zones into areas designated for social interaction and privacy. Private quarters seamlessly connect with outdoor gardens and terraces, fostering engagement with nature.
### Materiality and Energy Efficiency
The project's material choices prioritize sustainability and durability. Lavacrete, a recyclable 3D printing material, forms the structure's foundation, complemented by chilled beam systems that enhance energy performance through natural heating and cooling. Smart glass elements manage solar heat and light entry, while SIP insulated panels and terrazzo flooring provide aesthetic and thermal benefits. A robust photovoltaic solar panel system captures renewable energy, aligning with an energy-neutral objective. Water recycling systems further reduce consumption, contributing to the overall focus on environmental stewardship and occupant well-being through health-centric design features.