5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
The House of the Future is located in an urban setting and aims to redefine residential architecture by integrating functionality, sustainability, and contemporary design principles. With a clear focus on minimizing environmental impact while enhancing living efficiency, the structure is designed to accommodate current needs and allow for future adaptability.
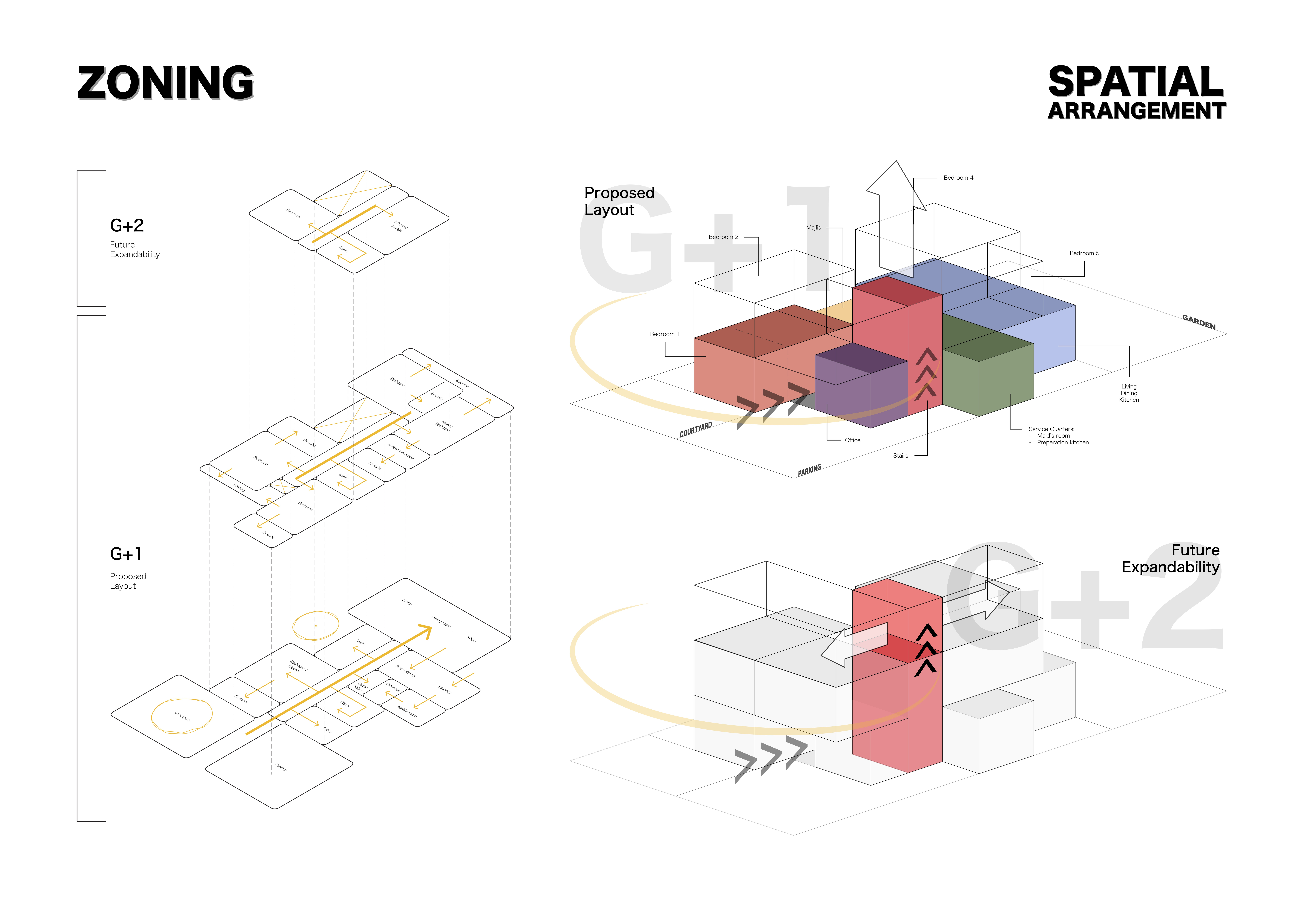
### Spatial Strategy and Layout
The spatial configuration features a two-level arrangement with an emphasis on distinct functional areas. The ground floor facilitates communal interactions, housing the kitchen, dining area, and living room, while the upper level provides private spaces, including multiple bedrooms with en-suite bathrooms. This thoughtful zoning allows for a dynamic lifestyle, with dedicated spaces for both social engagement and personal retreat. Future expansion options have been integrated into the structural system, enabling the addition of units without extensive modifications, thus addressing potential changes in occupancy needs over time.
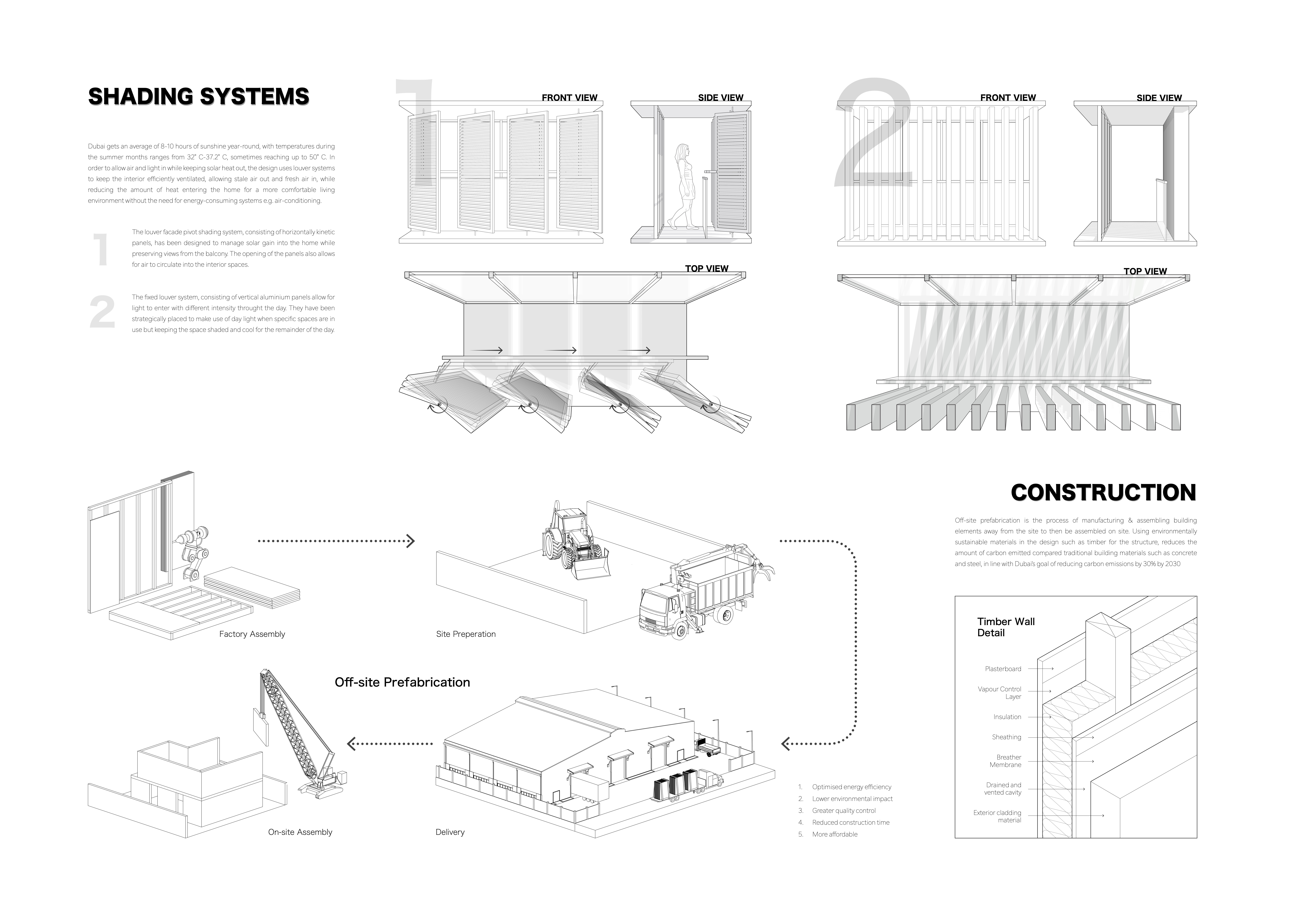
### Materiality and Construction Methodology
The facade composition is a deliberate amalgamation of concrete, wood, and glass, providing both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Concrete forms the primary support, while wood enhances the warmth and craftsmanship of external elements such as louvers and vertical slats. Expansive glass windows ensure ample natural light while integrating indoor and outdoor environments.
The construction methodology employs off-site prefabrication of structural components, optimizing quality control and reducing onsite assembly time. The use of an efficient timber wall system contributes to insulation and environmental sustainability, aligning with modern practices in energy conservation and waste minimization.