5 key facts about this project
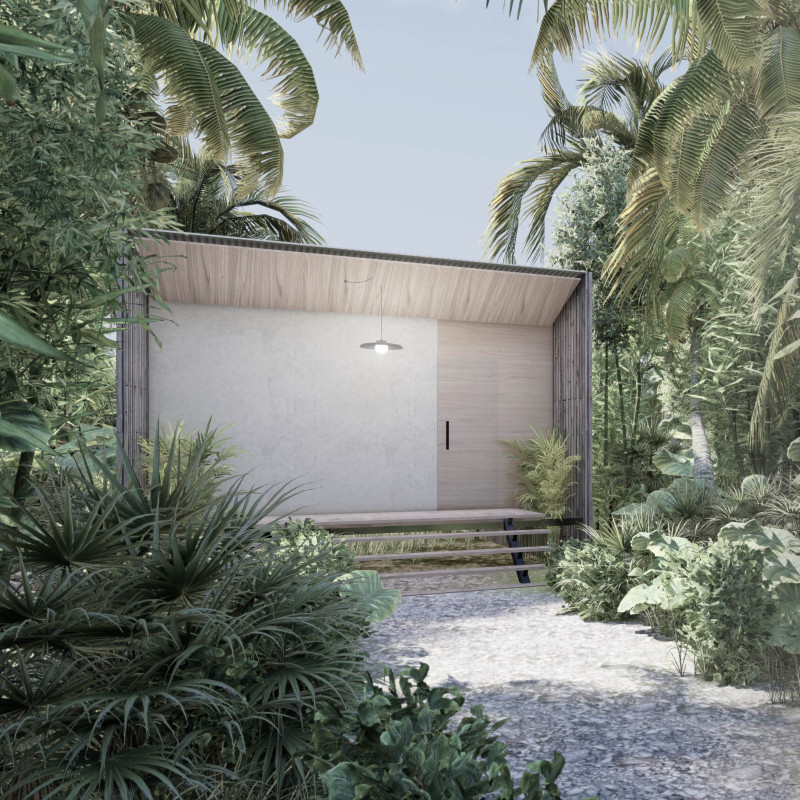
The huts are conceived as self-sufficient units meant to provide guests with temporary housing that facilitates both relaxation and engagement with nature. The layout consists of a series of clustered huts, each designed to blend seamlessly into their surroundings while offering privacy and comfort. The architectural design recognizes the importance of community interaction; therefore, a central community pavilion is included to encourage social activities among visitors.
Unique Design Approaches in Materiality and Sustainability
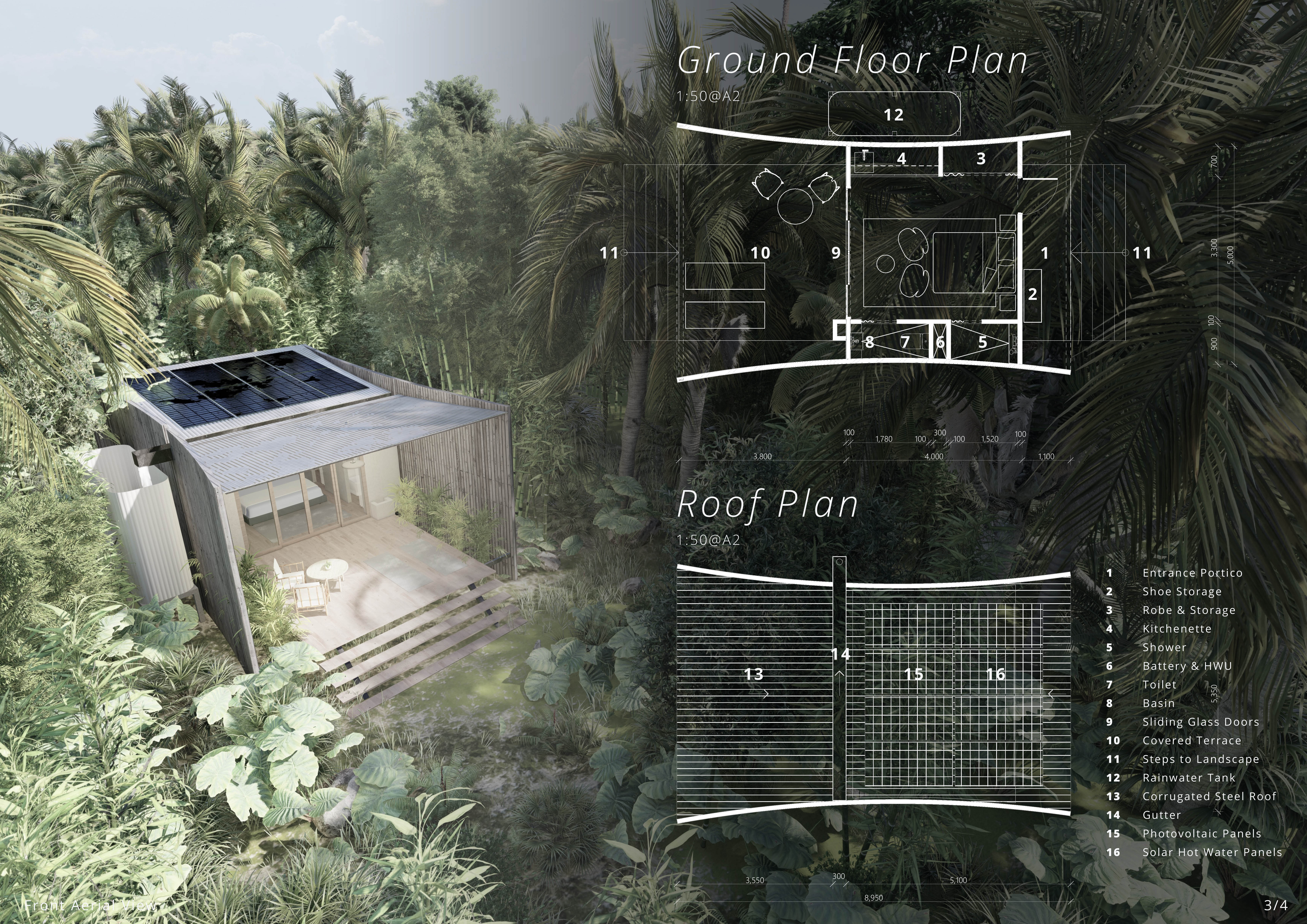
The architectural design employs a range of materials that are both environmentally friendly and contextually appropriate. Key materials include timber, concrete, steel, and glass. Timber is used for structural elements due to its lightweight properties and aesthetic appeal. Concrete serves as the foundation material, providing stability while minimizing visual impact. Corrugated steel roofing enhances durability while being lightweight. Large glass openings promote natural light and provide unobstructed views of the landscape, contributing to a cohesive indoor-outdoor integration.
The project implements several sustainable initiatives, including rainwater harvesting systems and solar energy solutions. By capturing rainwater and utilizing solar panels, the huts aim to minimize reliance on local resources and reduce overall energy consumption. Natural ventilation is achieved through strategically placed openings, enhancing indoor air quality without mechanical systems. This commitment to sustainability is a hallmark of the design, allowing for a lightweight ecological footprint.
Functional Layout and Innovative Spaces
The functional layout of each hut includes essential amenities such as a kitchenette, storage areas, a shower, and a toilet. The overarching design encourages cross-ventilation, making use of passive cooling methods that decrease the need for artificial climate control. Covered terraces extend living spaces into the landscape, allowing occupants to engage with the natural setting.
A notable feature is the integration of raised floors, which mitigate potential flood risks associated with seasonal rains. This design element not only provides safety but also enhances airflow beneath the structures, supporting the huts’ energy efficiency. Pathways are organically woven throughout the site, guiding guests through a sensory journey immersed in the native flora and fauna.
For further insights into this project, including architectural plans, sections, and designs, readers are encouraged to explore the comprehensive project presentation. This exploration will yield a more detailed understanding of the innovative architectural ideas implemented within the Cambodia Remote Hideout Huts.