5 key facts about this project
### Overview and Intent
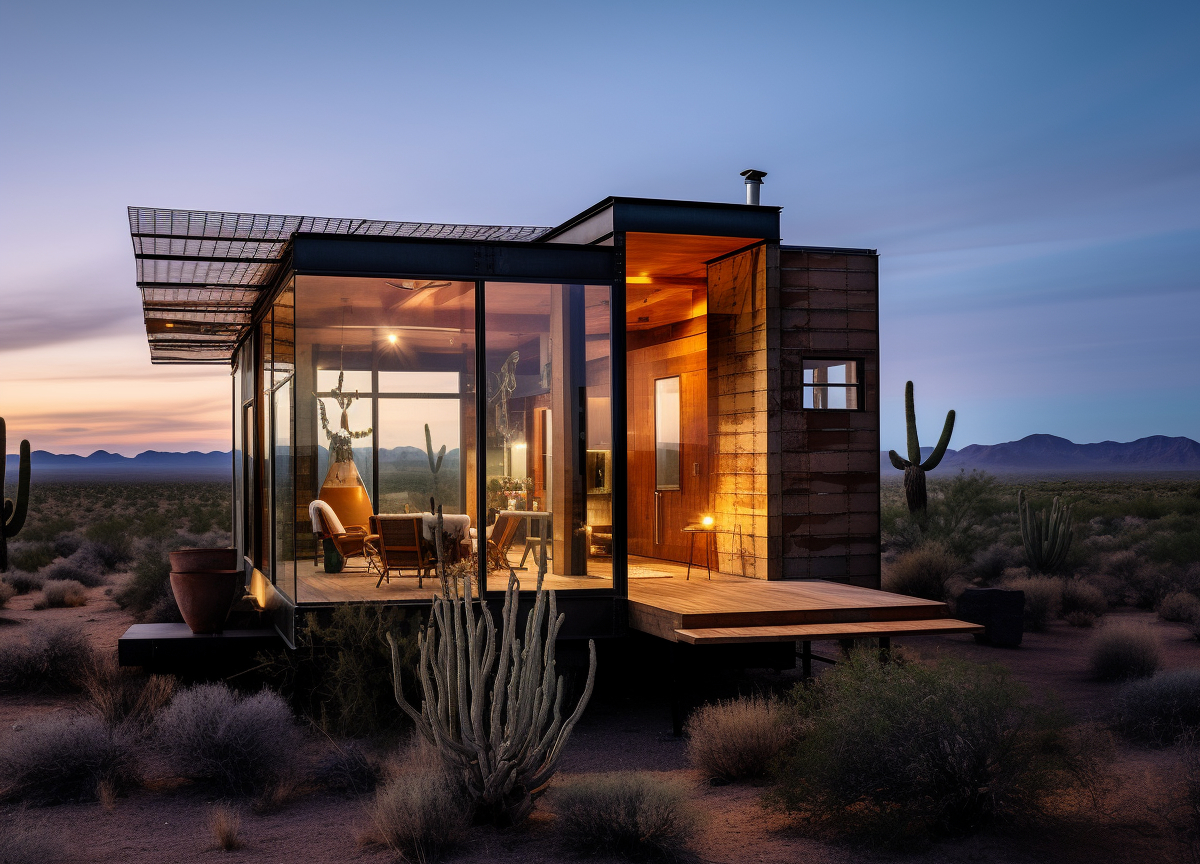
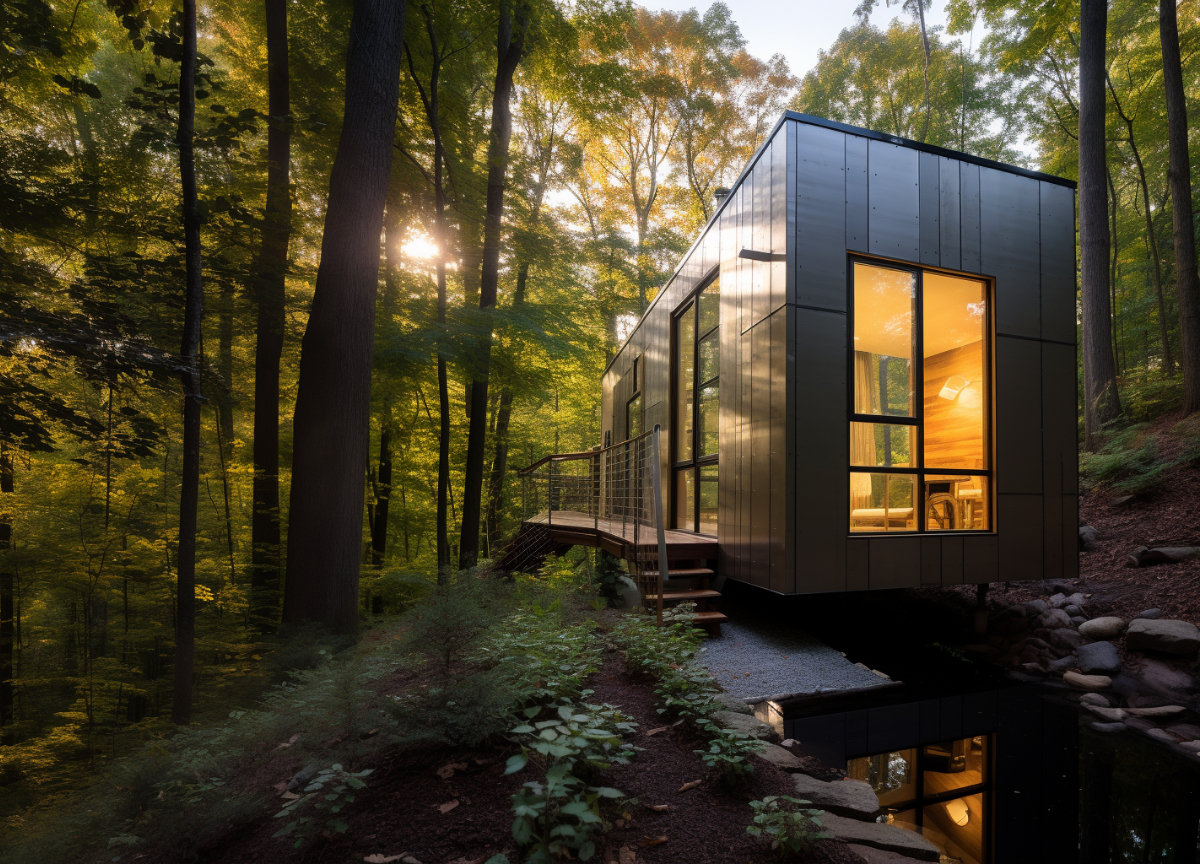
The Osaka Eco City project is designed to establish a sustainable urban environment in Osaka, Japan, emphasizing the integration of eco-friendly practices with modern urban living. The intent is to create a self-sustaining urban fabric that addresses environmental concerns while improving pedestrian accessibility and community engagement. This initiative aims to mitigate urban sprawl and enhance the quality of life through a balanced planning approach.
### Spatial Organization and Public Realm
A key aspect of the design involves the careful arrangement of infrastructure within the urban landscape to promote ecological responsibility. The separation of vehicular and pedestrian traffic minimizes congestion and enhances safety, utilizing dedicated pathways and streetscapes that encourage walking and cycling. Public urban areas and squares are central to the project, designed to facilitate social interaction and ecological functions. Functional green spaces such as parks and gardens are integrated into the layout, offering aesthetic, recreational, and environmental benefits, including green corridors that support biodiversity.
### Material Selection and Sustainability Practices
The architectural design incorporates various sustainable materials and construction techniques aimed at maximizing both aesthetic qualities and environmental performance. Notable materials include glass for facades to improve natural lighting, recycled concrete to minimize waste, and durable steel for innovative structural applications. Green roof systems are employed to enhance insulation and reduce heat absorption, while sustainable timber is utilized throughout the construction, reflecting a commitment to reducing ecological impact. This combination of materials underlines the project's dedication to sustainability while addressing the functional requirements of the urban environment.

 Adrianus Johannes J Van Oudheusden
Adrianus Johannes J Van Oudheusden