5 key facts about this project
Design Objectives and Unique Features
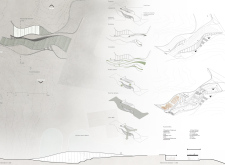
One of the distinguishing elements of "Sandskafl" is its dynamic roofline, which mimics the undulating surfaces of the landscape. This design approach not only enhances the visual appeal but also provides valuable natural ventilation and daylighting opportunities for the interior spaces. The extensive use of glass in the facade allows for panoramic views of the Icelandic scenery, promoting a connection between patrons and their environment while reducing reliance on artificial lighting.
Another notable aspect of the project is its emphasis on sustainable materials. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam beams form the primary structural components. These materials are selected for their energy efficiency and low carbon footprint, aligning with the overarching goal of reducing environmental impact. The incorporation of insulated glazing further enhances thermal performance, ensuring a comfortable atmosphere year-round.
Integration with the Environment
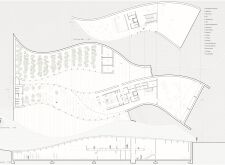
The layout of "Sandskafl" facilitates ease of movement and encourages social interactions through thoughtfully designed circulation paths. The building features areas designated for relaxation and gathering, offering visitors a multifunctional space that goes beyond conventional dining experiences. The design also responds to climatic challenges, with an architecture that effectively mitigates wind effects and enhances user comfort.
The green roof serves multiple purposes, including insulation, stormwater management, and fostering local biodiversity. This biophilic approach not only addresses functional objectives but also reinforces a connection to the natural landscape, positioning "Sandskafl" as a model of responsible architecture.
For further insights into the "Sandskafl" project, including architectural plans, sections, and detailed design elements, readers are encouraged to explore the full documentation of this innovative endeavor. Investigating these architectural aspects can provide a deeper understanding of the project’s contributions to contemporary design and its significance within the context of sustainable architecture.