5 key facts about this project
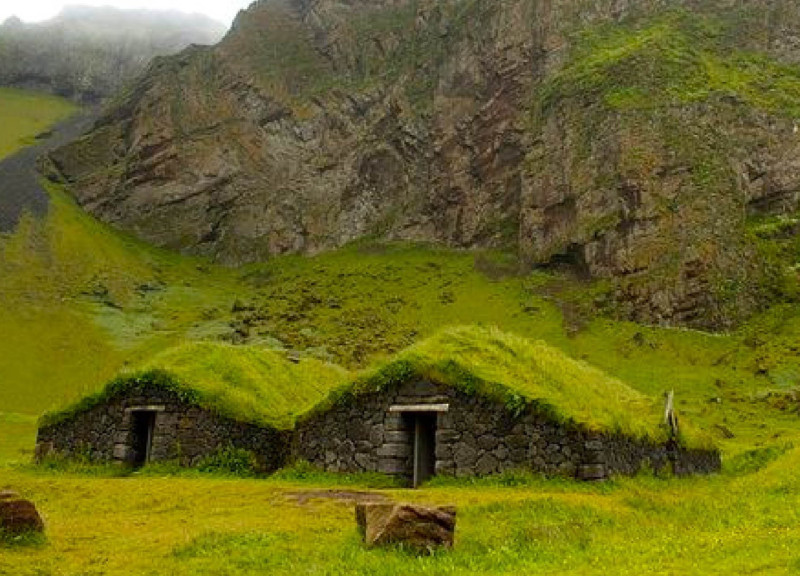
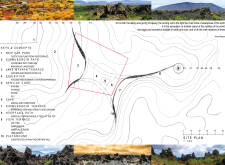
Functionally, the Dimmuborgir Landscape Project serves multiple purposes that cater to visitors. It provides essential amenities, such as parking, restrooms, and food service, while also creating a framework for educational experiences about the area's unique ecology and geology. The design includes several interconnected areas, each serving a specific function yet seamlessly integrated into the landscape. The new car park is strategically placed to minimize visual impact, allowing the natural scenery to remain uninterrupted. The Dimmuborgir Path, accessible for all, encourages exploration of the stunning surroundings, enhancing the visitor’s connection with nature.
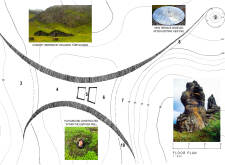
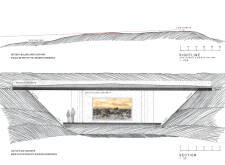
Several key architectural elements define this project. The Dimmuborgir Path connects various sites and landscapes, facilitating an immersive experience that allows guests to engage directly with the diverse ecosystem. The Lake Mývatn Terrace acts as a communal gathering space, offering visitors a place to relax while taking in the views. Meanwhile, the exhibition space is crucial for providing educational information about the region, highlighting its ecological significance.
The service core is another critical component, housing kitchen facilities, storage, and restrooms, ensuring visitor comfort without detracting from the overall aesthetic. A thoughtfully designed café provides a venue for refreshment and social interaction, enhancing the overall visitor experience. Additionally, the Dimmuborgir Terrace creates opportunities for taking in expansive views of the unique geological formations, while the Hverfjall Path leads visitors upwards, offering different perspectives of the striking landscape.
Playfulness is embraced through the incorporation of a playground situated within an earthen wall that complements the surrounding geography. This design approach encourages children to engage with their environment while remaining visually discreet.
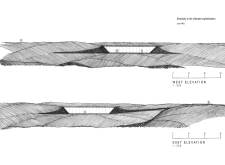
The material choices in the Dimmuborgir Landscape Project reflect a commitment to sustainability and environmental harmony. The use of cast-in-place concrete, which offers both durability and aesthetic integration with the earth, is indicative of a broader philosophy that considers the life cycle and ecological footprint of materials. Precast concrete elements enhance efficiency, while earth-sourced aggregates serve to minimize transportation impact, aligning with modern principles of sustainability.
What makes this project unique is its emphasis on an integrated visitor experience that balances architectural form with natural beauty. The design does not merely create structures; it actively engages the environment and invites people to appreciate the indigenous landscape. Elements like the pathway system and communal spaces encourage reflection and connection with the surroundings, creating an enriching experience that transcends traditional architectural expectations.
The Dimmuborgir Landscape Project stands as an exemplary model of how architecture can enhance the understanding and appreciation of natural environments. It invites visitors to engage with both the site and their surroundings in meaningful ways. For those interested in exploring the project's detailed architectural plans, sections, and innovative designs further, a closer examination of its presentation will provide deeper insights into this thoughtful architectural endeavor.