5 key facts about this project
### Overview
The Prefab Ecohouse project is situated in the United Arab Emirates and aims to address contemporary housing demands through a sustainable and efficient design. The project integrates modern construction practices with cultural references to traditional Arab architecture, focusing on minimizing environmental impact while fulfilling the needs of modern living. It emphasizes adaptability in the spatial organization and the selection of materials, catering to evolving family dynamics in a rapidly changing urban landscape.
### Spatial Organization
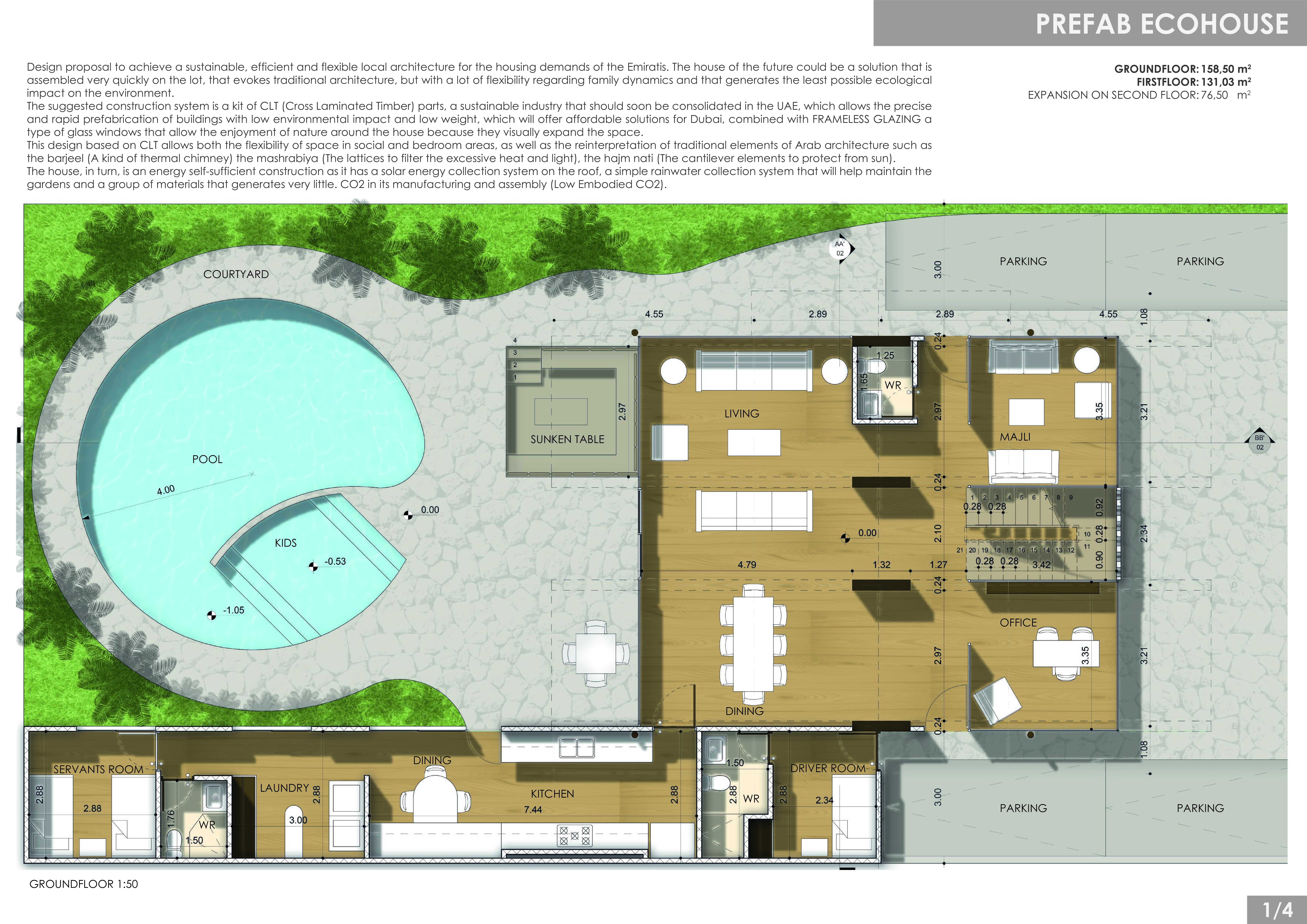
The spatial arrangement of the Prefab Ecohouse is designed with a clear focus on functionality and social interaction. The ground floor integrates essential living spaces, such as the living room, dining area, and kitchen, all linked to an outdoor sunken table and pool area that promotes outdoor engagement. Private areas, including service rooms, are discreetly incorporated to maintain a harmonious living environment.
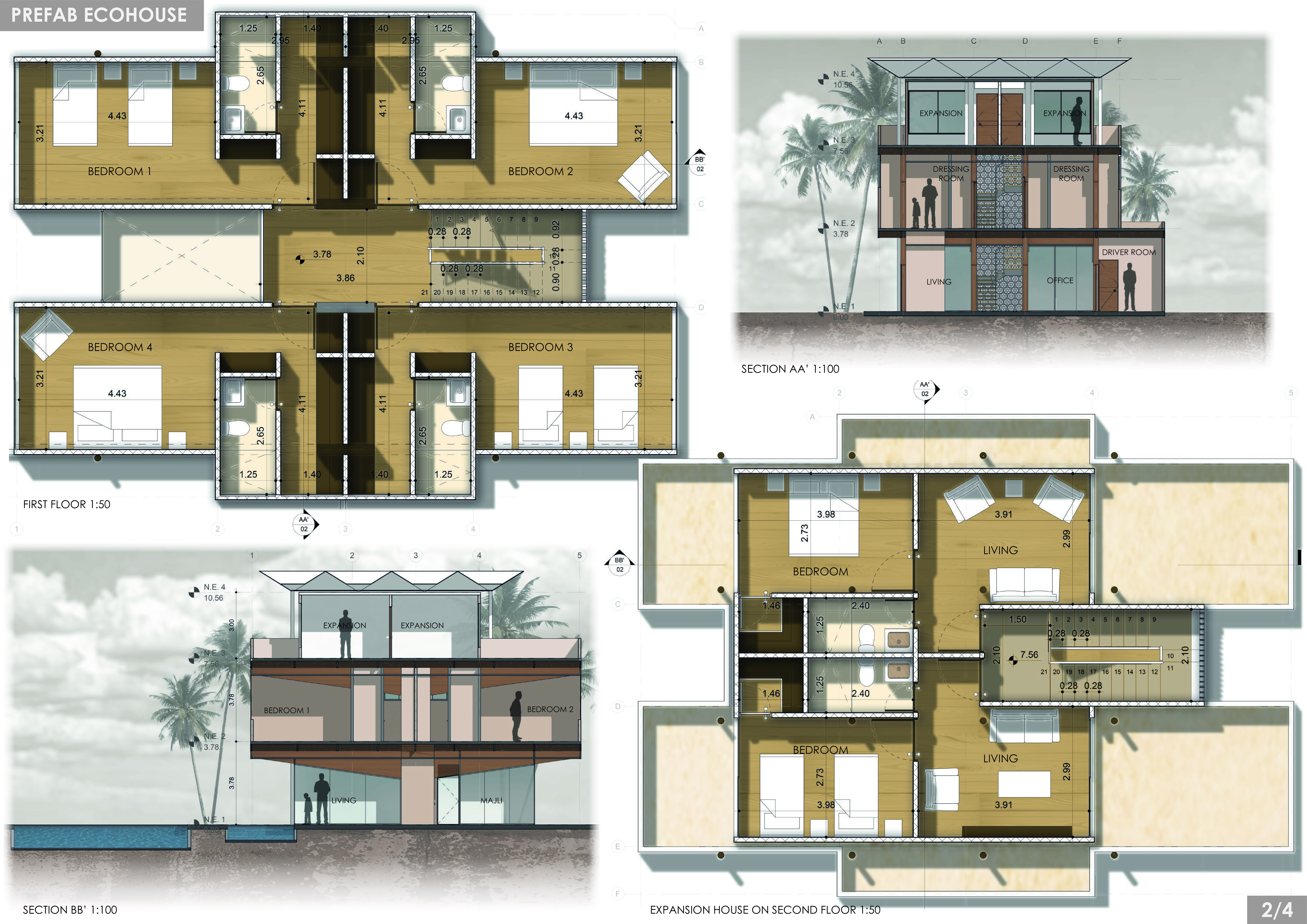
On the first floor, four bedrooms are strategically positioned to ensure privacy while fostering communal connections through shared spaces. This arrangement reflects traditional values while accommodating contemporary family needs. The design also allows for potential future expansion, showcasing a flexible approach to residential living that responds to the changing requirements of its occupants.
### Materiality and Sustainability
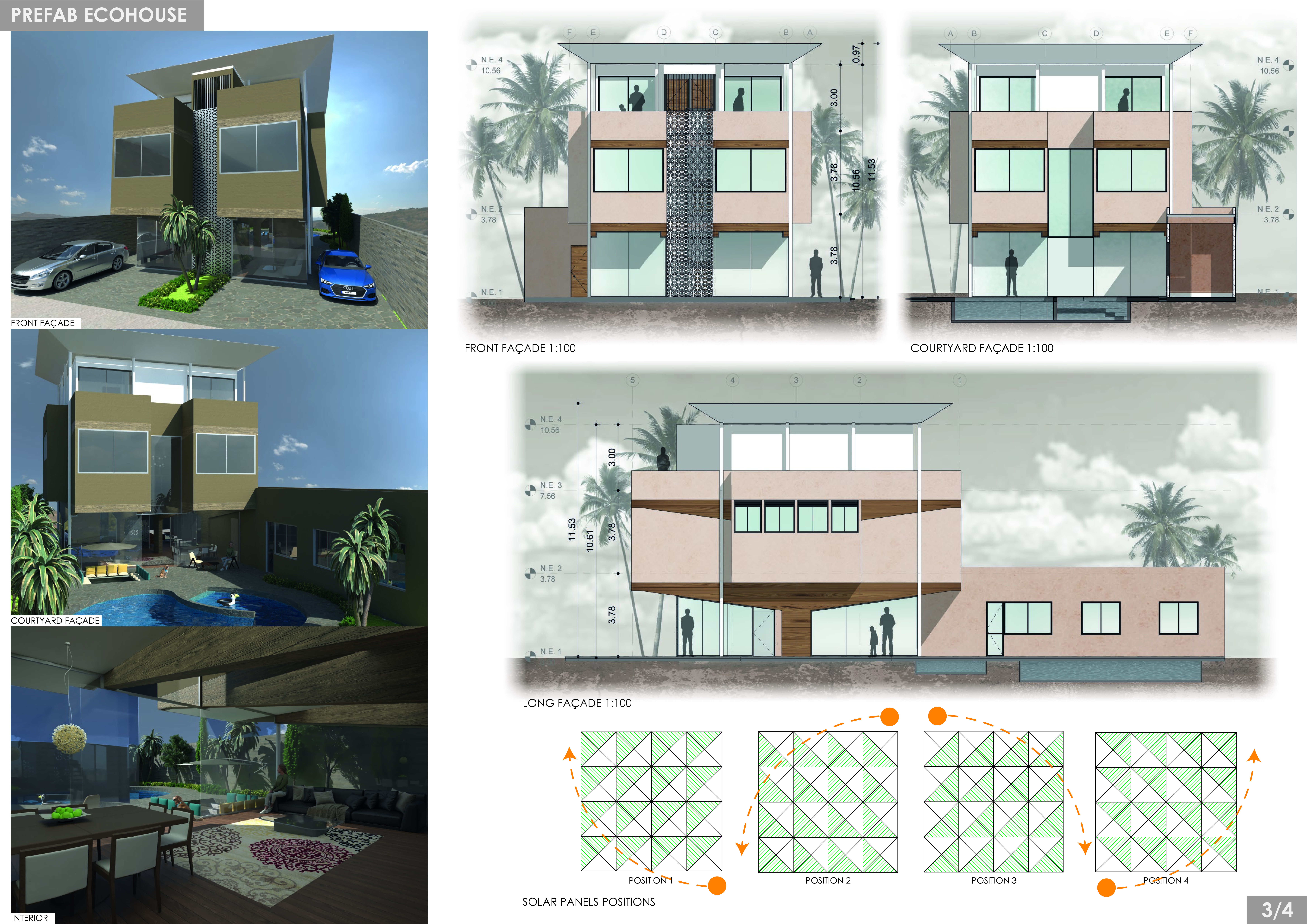
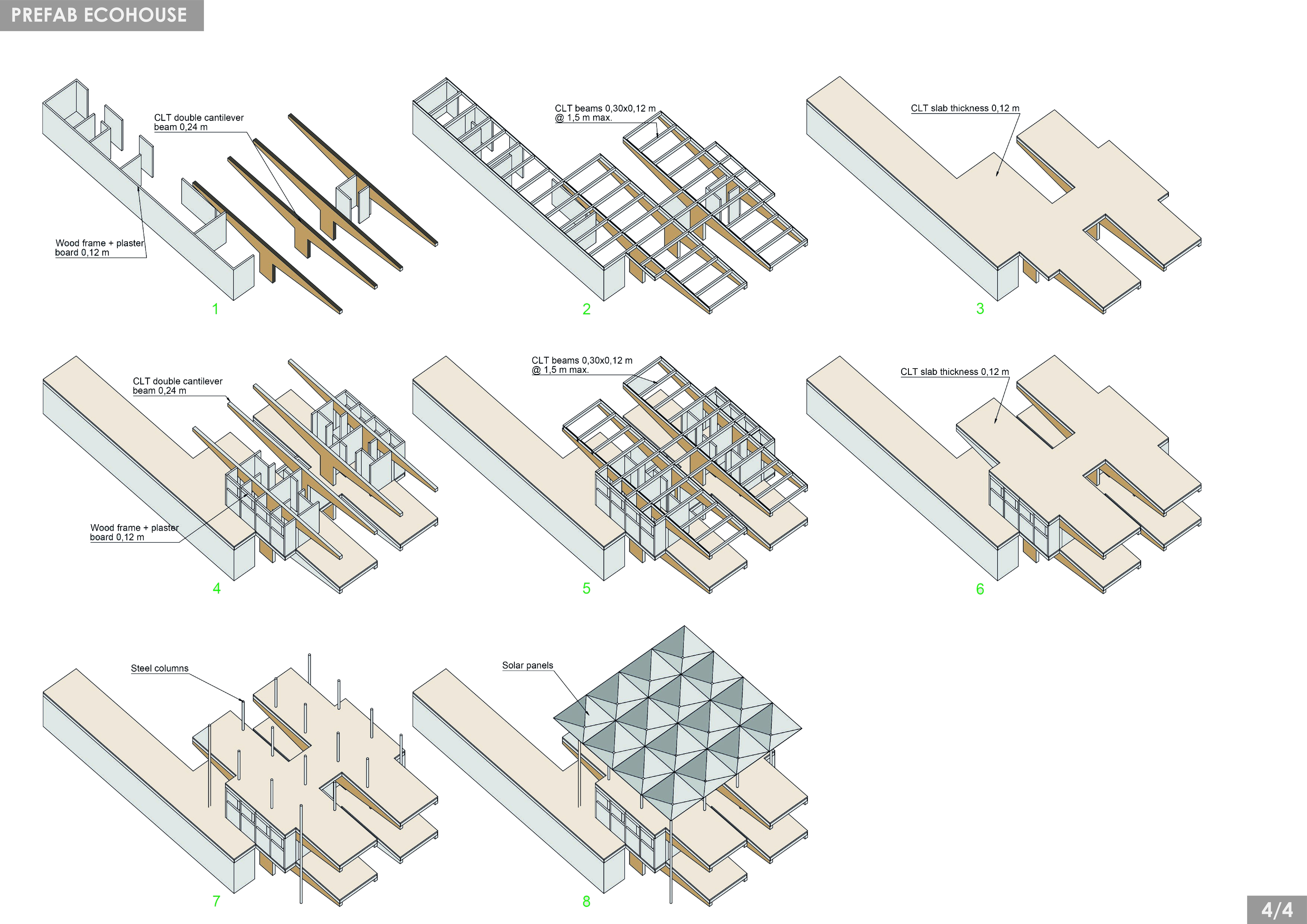
The Prefab Ecohouse employs a set of sustainable materials that contribute to its ecological narrative. Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) serves as the primary structural element, providing strength and thermal efficiency, which facilitates fast construction timelines. Additionally, the use of frameless glazing maximizes natural light and enhances the continuity between indoor and outdoor environments.
A rainwater collection system is incorporated to support self-sufficiency in the arid climate of the UAE, while strategically placed solar panels contribute to energy independence. The selection of low embodied carbon materials further reduces the ecological footprint of the construction process. Together, these features create a cohesive sustainability framework that addresses the region's environmental challenges while offering an efficient and responsive living solution.