5 key facts about this project
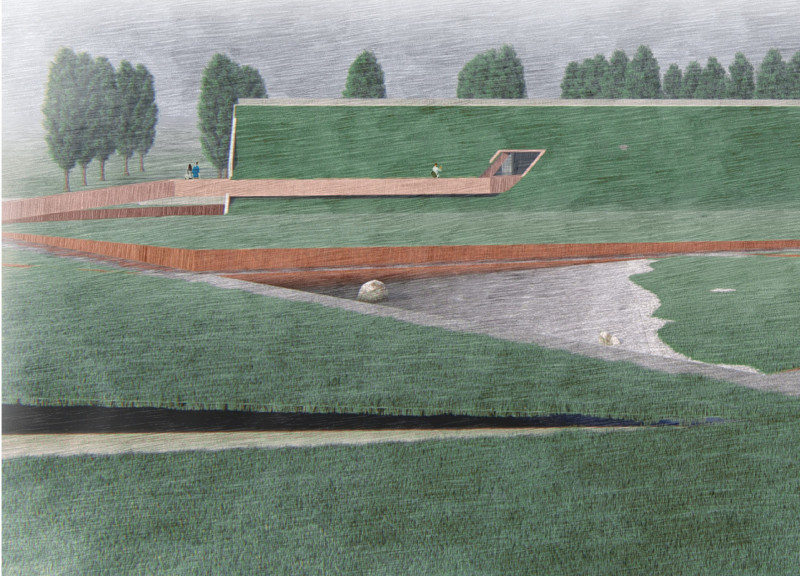
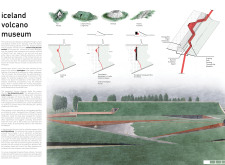
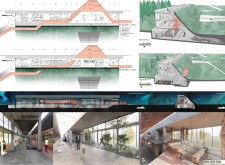
The museum is strategically located to take advantage of its unique geographical context, situated in an area known for its volcanic landscape. The design promotes visitor engagement and interaction with the exhibits, which detail the history and science behind Iceland’s volcanoes. The building’s orientation and placement maximize views of both the natural surroundings and the internal gallery spaces.
Spatial Configuration and Layout
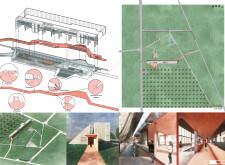
The museum’s layout is characterized by an elongated form that follows the contour of the land. This design approach minimizes disruption to the natural landscape while facilitating a clear flow of movement throughout the facility. Key spaces include:
- Exhibition Areas: Designed to showcase interactive displays that educate visitors about volcanic activity, the exhibition spaces are adaptable to accommodate various temporary exhibits.
- Café and Visitor Amenities: These components are integrated seamlessly into the structure, offering spaces for rest and reflection, while ensuring that the overall experience remains focused on the museum’s educational mission.
Materials and Construction Techniques
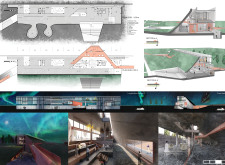
The construction employs a combination of concrete, glass, wood, and stone, each selected for its contextual relevance.
- Concrete provides structural integrity and allows for sculptural forms, while glass is utilized to create visual transparency that invites natural light into the building, enhancing visitor experience.
- Wood elements are incorporated in finishes, contributing warmth and a connection to Iceland’s traditional building techniques.
- Stone, reflecting volcanic geology, grounds the structure within its landscape while reinforcing the educational narrative surrounding Iceland’s geological features.
Innovative Design Approaches
The architectural design integrates various innovative approaches that distinguish the Iceland Volcano Museum. One key aspect is the use of green roofing that blends with the environment, promoting sustainability while also enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the building.
The incorporation of pathways that meander through the site encourages exploration and discovery, allowing visitors to engage with both indoor and outdoor exhibits seamlessly. Observation points are strategically placed to capture views of significant geological features, ensuring that visitors can appreciate the natural beauty of Iceland alongside the curated collections within the museum.
The design prioritizes flexibility, allowing for the exhibition spaces to adapt over time as new scientific discoveries emerge or as community needs change. This adaptability ensures the relevance of the museum as an educational institution, positioning it as a vital resource for both locals and tourists.
For more detailed insights into the architectural plans, sections, designs, and ideas that shaped this project, interested readers are encouraged to explore the project presentation further. The perspectives offered in those documents provide greater context to the architectural decisions made throughout the design process, reflecting the intentions of the project in relation to its unique geographical setting and cultural significance.