5 key facts about this project
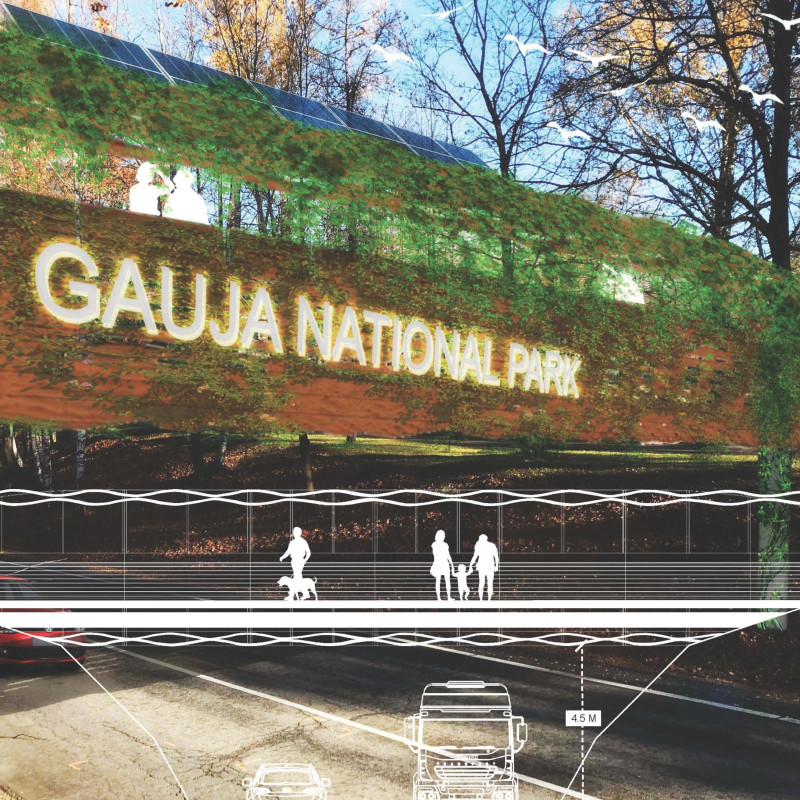
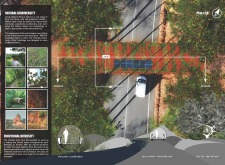
The footbridge serves as a critical link for pedestrians, promoting exploration and accessibility within the expansive park. It invites visitors to traverse through the lush greenery while maintaining a focus on ecological sensitivity. The architectural design functions as a conduit, facilitating the movement of people while encouraging moments of contemplation and interaction with the diverse ecosystems present in the park.
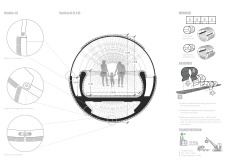
Central to this architectural design is the modular structure composed of prefabricated elements that collectively embody the spirit of the landscape. The primary materials used, including recycled steel tubing and reclaimed thermal wood, reflect a commitment to sustainability and ecological mindfulness. This choice of material not only underscores the environmental considerations of the project but also adds a tactile quality that resonates with the natural elements surrounding the bridge.
The footbridge features a thoughtfully designed canopy that mimics the natural formations of foliage. This unique architectural approach offers shade and shelter while allowing filtered sunlight to enhance the experience of users. The integration of solar panels into the structure provides a means of renewable energy, underpinning the project's commitment to environmentally responsible design. By harnessing solar power, the footbridge illuminates the way for visitors at night without relying on traditional energy sources, showcasing a forward-thinking approach within contemporary architecture.
One of the most distinguishing aspects of this project is the incorporation of dynamic observation pods along the bridge. These pods serve as resting areas and vantage points, encouraging users to pause, reflect, and engage with their surroundings. Each pod is designed to adapt to the varying elevations of the landscape, providing diverse perspectives and enhancing the visitor experience. This attention to detail in crafting inclusive spaces highlights the architects’ emphasis on user interaction with the natural environment.
In addition to its functional attributes, the architectural design fosters an educational platform regarding the park's rich biodiversity. Informational signage and lighting are integrated discreetly throughout the structure, guiding visitors while enhancing their understanding and appreciation of the ecosystem. This collaborative design approach emphasizes a harmonious relationship between architecture and nature, encouraging responsible enjoyment of the park.
The architectural design reflects a unique methodology that prioritizes ecological integration, combining aesthetic refinement with practical considerations. By weaving the structure into the fabric of Gauja National Park, the project presents a compelling case for environmentally responsive architecture. The emphasis on modularity and sustainability highlights innovative architectural ideas that can be adapted to various contexts, allowing this project to serve as a model for future developments in natural settings.
To gain a deeper understanding of the project, readers are encouraged to explore the architectural plans, sections, and design details, which provide valuable insights into the nuances and thought processes behind this innovative architectural endeavor.