5 key facts about this project
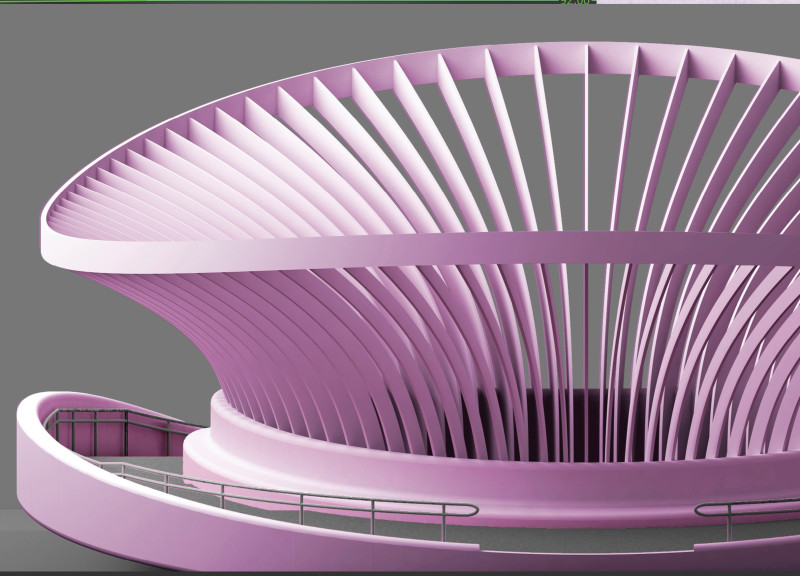
From a functional perspective, the bridge serves as a vital pedestrian route, facilitating movement and enhancing accessibility for visitors. Measuring 28 meters in width and extending to a total length of 41 meters, the structure combines practicality with visual appeal. This duality is achieved through a bionic form that resembles organic lines found throughout the park, reinforcing its connection to the landscape while offering pedestrians a safe and pleasant experience.
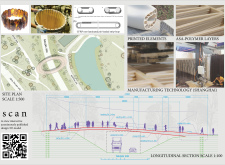
The materials chosen for the project play a critical role in its overall effectiveness. Crafted from Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) polymer, the bridge leverages the advantages of 3D printing technology, allowing for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional construction methods. The design incorporates modular components that facilitate on-site assembly, minimizing environmental impact and reducing construction time. Complemented by Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer tendons, the bridge ensures structural integrity while maintaining a lightweight profile. The inclusion of these advanced materials speaks to the project's commitment to sustainability, as the application of recyclable materials in future iterations aligns with the growing emphasis on environmentally responsible architecture.
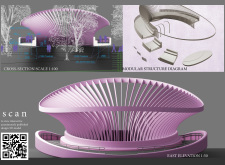
Key design elements highlight the innovative approaches used in the project. The bridge's slatted structure provides an interplay of light and shadow, creating an inviting atmosphere for pedestrians. This dynamic feature not only enhances the aesthetic qualities of the bridge but also promotes a connection with the environment, allowing visitors to experience the landscape in a new light. The careful design of ramps and landings throughout the structure ensures that it meets accessibility standards while maintaining a coherent visual narrative.
Moreover, the project represents a thoughtful exploration of the potential for 3D printing in architecture. As one of the largest pedestrian bridges constructed through this method, it serves as a case study for future designs aiming to harness the advantages of digital fabrication. The modular approach allows for creative flexibility, paving the way for further innovation within the field.
The architectural plans and sections of the bridge illustrate its complexity and thoughtful design. These technical drawings provide insights into the intricacies of the structure and underline the attention to detail that informs the project. As visitors engage with the bridge, they encounter not only a form of transportation but also an interactive work of art that enhances their understanding of the natural surroundings.
When examining the architectural ideas presented in this project, it is clear that the design seeks to establish a harmonious balance between human activity and the environment. The bridge acts as a mediator, facilitating movement while simultaneously encouraging a deeper appreciation for the park’s natural beauty. This project stands as a testament to the evolving relationship between architecture and technology, showing how contemporary design can respond thoughtfully to ecological contexts.
For a more detailed understanding of this innovative architectural undertaking, readers are encouraged to explore various elements, including architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs. Engaging with these details will provide a thorough insight into the project's unique contributions to the field of architecture.