5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
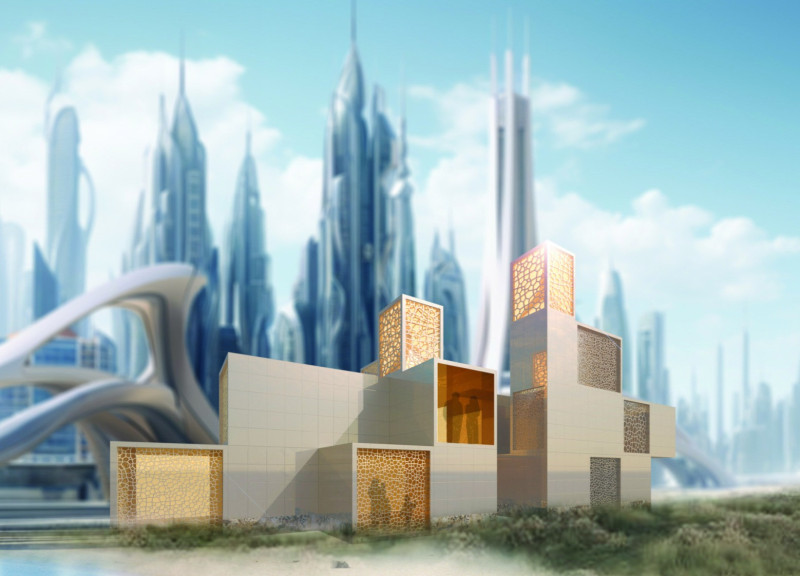
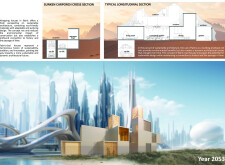
"Woven Abode" is situated in Dubai, a region characterized by a challenging climate that necessitates innovative architectural solutions. The design of the structure incorporates fabric as a primary material, merging traditional architectural influences with contemporary technological applications. This approach facilitates an interaction between the building and its environment, positioning the structure as both a functional dwelling and a responsive entity reflective of its cultural and historical context.
## Materiality and Sustainability
Central to the design is the use of sustainable materials that promote environmental stewardship and adaptability. Biodegradable fabric serves as the primary façade, allowing the structure to evolve naturally over time. Organic cotton is selected for its thermal properties, contributing to energy efficiency, while hemp and recycled textiles minimize the carbon footprint associated with construction. Steel is utilized for the support framework, ensuring durability and structural integrity, complemented by glass elements that enhance natural light and ventilation.
The architectural design emphasizes energy efficiency through natural insulation, daylight optimization, and improved indoor air quality. The components of the design allow for deconstruction and recycling, ensuring sustainability throughout the building’s lifecycle. By integrating innovative materials with a focus on environmental impact, "Woven Abode" establishes a model for future architectural endeavors.
## Spatial Configuration and Community Interaction
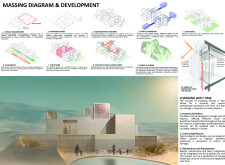
The layout of "Woven Abode" features modular spaces arranged around a central courtyard, fostering a sense of community while maintaining privacy for residents. A standardized 3x3 meter module facilitates a variety of spatial configurations, addressing diverse functional requirements. The orientation of living areas around the courtyard enhances connectivity and promotes cross-ventilation, crucial for adapting to Dubai's climate.
Architectural elements such as vaulted ceilings and wind towers enhance natural ventilation, combating heat while enriching the interior environment. The dynamic fabric cladding not only contributes to the building's aesthetic but also accommodates seasonal changes, reinforcing the adaptability of the structure in response to environmental conditions.