5 key facts about this project
In terms of function, OOBMAB provides essential living spaces, including sleeping areas, a kitchen, and a compact bathroom. The internal layout is designed to maximize utility while ensuring comfort for its inhabitants. Each area is organized with a clear purpose in mind, allowing researchers to effectively conduct their work while maintaining a supportive living environment. The architectural design embraces the notion of adaptable spaces that can cater to various activities without compromising the experience of living in harmony with nature.
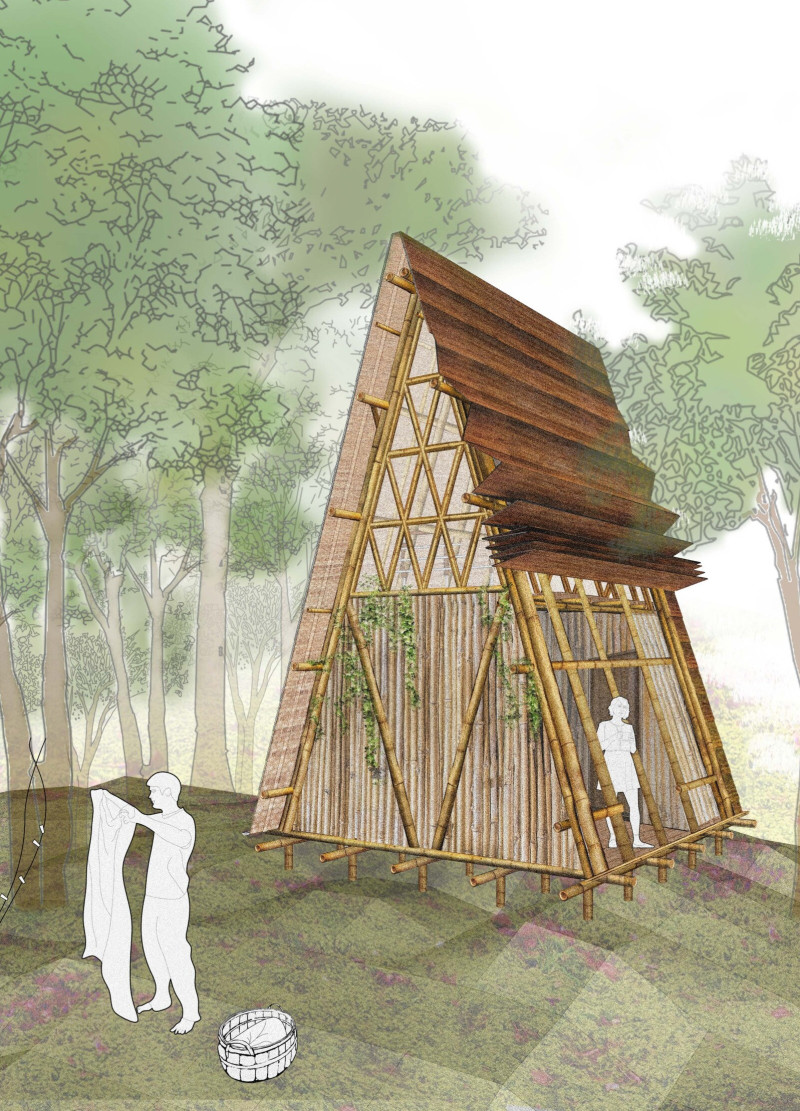
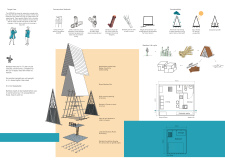
The structure’s distinctive triangular form and open framework borrow elements from local vernacular architecture while integrating modern materials and techniques. The primary material used in the construction is bamboo, selected for its sustainability and strength. Given its rapid growth and availability within the region, bamboo provides an ecologically sound option that aligns well with the project’s goals of minimal environmental impact. This choice of material also enhances the aesthetic quality of the design, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere for its occupants.
Details such as the use of rubber tree oil for waterproofing ensure the durability of bamboo elements against the humid climate. Woven bamboo mats are utilized for insulation, aiding in temperature regulation without the need for mechanical systems. Laminated bamboo planks serve as flooring, which is not only practical but also aesthetically pleasing. The inclusion of mesh coverings in window openings allows for visibility and airflow while maintaining security. Furthermore, the rainwater collection pipes reinforce a sustainable approach to resource management, ensuring that the occupants have access to water without relying on external sources.
What distinguishes the OOBMAB project is its emphasis on a lightweight construction method designed for rapid assembly and disassembly. The use of strings and dowels for connections enables easy relocation, making it an ideal solution for researchers who may need to move frequently. The design allows for the structure to be elevated above ground, accommodating natural terrain variations and providing protection from the elements. This modularity speaks to a broader trend in architecture that prioritizes flexibility and adaptability in response to evolving needs.
Additionally, the incorporation of sustainable features such as solar panels for renewable energy and a composting toilet for efficient waste management highlights the project's commitment to environmental stewardship. Each element is meticulously considered to ensure that the structure not only meets the immediate needs of its occupants but also contributes to the broader ecological balance of the rainforest.
The architectural ideas presented in OOBMAB are reflective of a growing consciousness in the field of design regarding the importance of sustainability and ecological sensitivity. This project serves as a case study for how architecture can harmonize with nature, utilizing local materials and technologies to create spaces that are both functional and environmentally responsible.
For those interested in delving deeper into the complexities of OOBMAB, it is recommended to explore the architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs that provide a comprehensive view of the project. These insights can enhance understanding of the innovative thinking behind its architecture and inspire further exploration of sustainable design practices in similar contexts.