5 key facts about this project
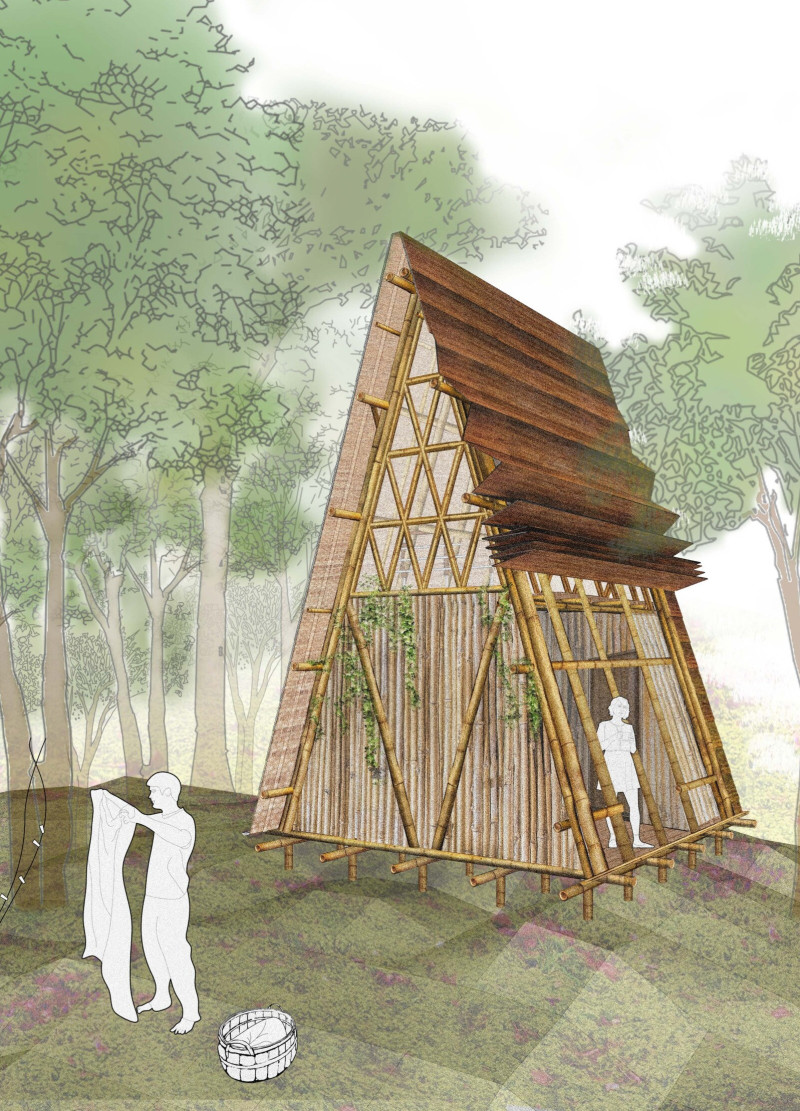
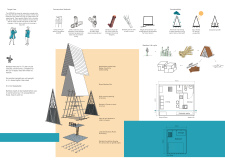
The OOBMAB project is an architectural design focused on creating temporary housing for researchers conducting field studies in the Malaysian rainforest. Its primary goal is to provide a functional and adaptable structure that meets the specific needs of occupants while minimizing environmental impact. The design utilizes sustainable materials and an innovative approach to construction, contributing to both the building's utility and its ecological footprint.
Sustainable Material Use The OOBMAB project stands out due to its extensive use of bamboo, a material recognized for its strength, light weight, and sustainability. Bamboo's rapid growth and renewability make it an ideal choice for temporary structures. The design incorporates various forms of bamboo, including laminated bamboo planks for flooring, woven bamboo mats for wall surfaces, and structural bamboo beams that form the main framework. These materials not only reduce the project's carbon footprint but also enable a quick assembly and disassembly process, facilitating mobility for researchers.
Another noteworthy feature of OOBMAB is the integration of other eco-friendly elements such as rubber tree oil for waterproofing, mesh screening for insect protection, and a rainwater harvesting system. These features enhance the project's sustainability and contribute to a low-impact living environment.
Functional Design Elements The OOBMAB project employs a simple A-frame design that allows for efficient water runoff and provides structural stability against tropical weather conditions. The open interior layout promotes natural ventilation and maximizes the use of natural light, creating an inviting atmosphere for occupants. The design also includes large windows and adjustable openings that facilitate airflow while maintaining a strong connection to the surrounding landscape.
The project incorporates a flexible foundation capable of adjusting to varying terrain, ensuring stability in the diverse topography of the rainforest. The construction methods employed, such as string techniques and dowel systems, simplify assembly and increase the building's adaptability for different locations.
Innovative Integration of Systems Additionally, OOBMAB integrates various sustainable technologies that enhance its functional capabilities. Solar panels are included to provide renewable energy, reducing dependency on external power sources. The project also features composting toilets, which minimize water usage and promote waste recycling, aligning with the overall emphasis on sustainability.
The combination of these systems not only supports the day-to-day operational needs of researchers but also exemplifies a forward-thinking approach to residential architecture in ecologically sensitive regions.
For additional insights into the OOBMAB project, including architectural plans and sections, readers are encouraged to explore the comprehensive presentation of this design. By examining these details, one can appreciate the full scope of the architectural ideas and innovations that define this unique project.